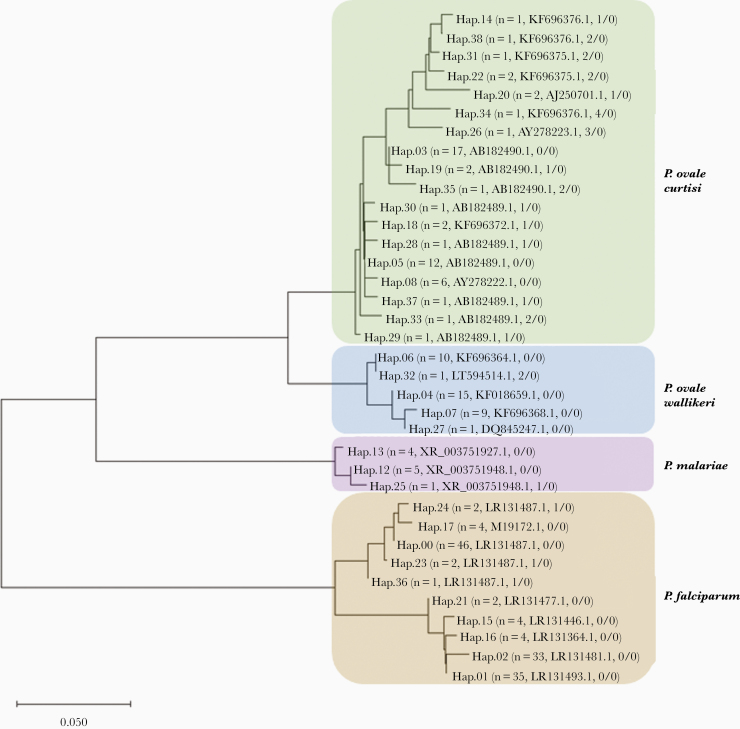
Figure 3.
Neighbor-joining tree of genetic relatedness across the 35 haplotypes identified from pooled amplicon deep sequencing results of 62 Plasmodium ovale polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-positive samples. Each unique haplotype is numbered and branches of the tree for each malaria species are laid over a color (brown, P. falciparum; purple, P. malariae; blue, P. ovale wallikeri; and green, P. ovale curtisi). In parentheses after the haplotype number is the number of samples that contained the haplotype, the GenBank accession name for closest match, and the number of single nucleotide polymorphisms/number of indels difference in the haplotype from the closest GenBank reference. Twenty-three samples (37%) were positive for P. ovale curtisi, 16 (26%) were positive for P. ovale wallikeri, and 3 (5%) contained both P. ovale curtisi and P. ovale wallikeri. However, given that the malaria genome contains multiple copies of the 18S gene, samples may contain more than 1 haplotype of a species. The scale bar represents the number of base substitutions per site.