Fig. 10.
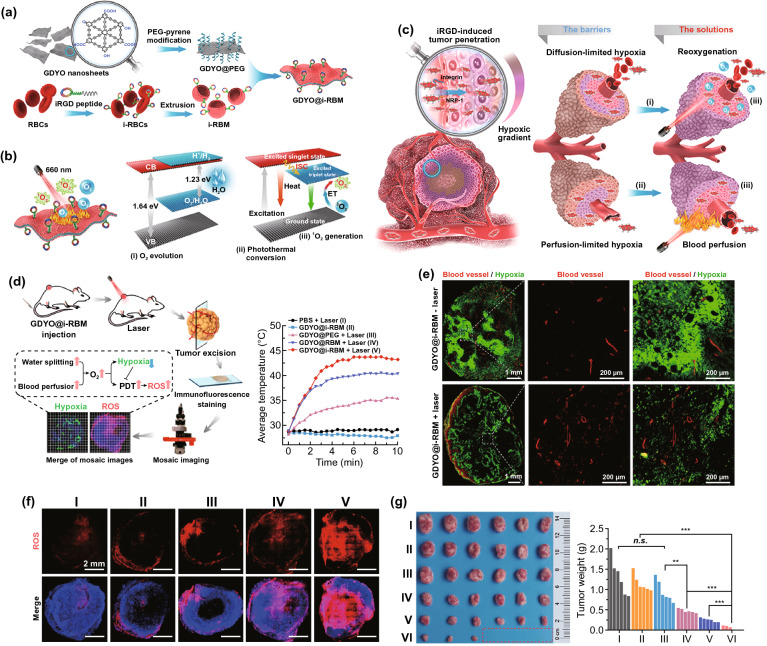
a Schematic illustration of the synthetic process of GDYO@iRBM. GDYO@i-RBM was obtained by coating PEG functionalized GDYO nanosheet with i-RBM, which were extracted from iRGD anchor-modified RBCs followed by extrusion through a porous membrane. b Schematic illustration of the working principles of GDYO@i-RBM. c i-RBM on the surface of GDYO facilitates the accumulation and deep penetration in the tumor. Meanwhile, under 660 nm laser irradiation, O2 evolution and hyperthermia caused by GDYO can overcome O2-diffusion-limited and perfusion-limited hypoxia barriers and lead to efficient PDT ablation of tumors. d Schematic illustration showing the evaluation of hypoxia and 1O2 levels in tumor, and temperature increase of the tumors upon irradiation. e Hypoxia immunofluorescence and vessel morphometric analyses of tumor slices. The blood vessels and hypoxia regions were stained with anti-CD31 antibody (red) and hypoxia probe (green), respectively. f Representative ROS fluorescence images of tumor slices. g Photos and weight of the tumor tissues obtained on day 22 post-treatment.
Reproduced with permission from Ref. [224]