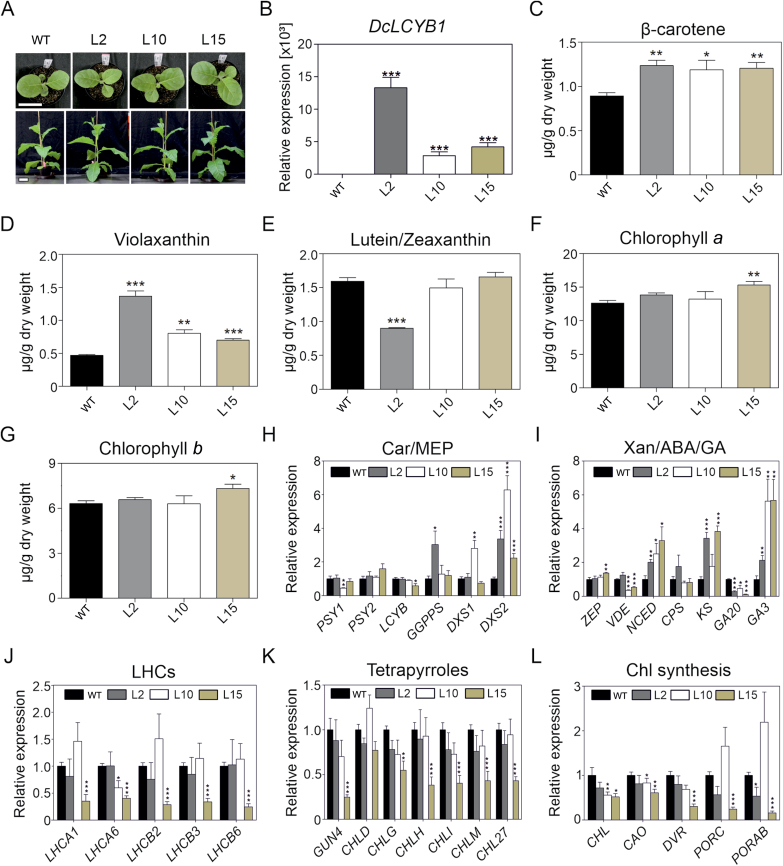
Fig. 2.
Highly increased DcLCYB1 expression causes no changes in phenotype but increases pigment content and affects gene expression in tobacco plants. (A) Two-week-old (upper) and 4-week-old (lower) transplastomic and wild-type plants. Scale bar: 10 cm. (B) DcLCYB1 expression levels measured by qPCR. (C–G) Pigment content (carotenoids and chlorophylls) measured by UPLC. (H–L) Gene expression analysis of carotenoid and carotenoid-related pathways. The expression of Actin as a stable reference gene was used for normalization. Increases, decreases and/or no change in all three lines for the majority of the genes involved in carotenoid, MEP, chlorophyll, GA, LHC, and tetrapyrrole pathways were observed. Columns and bars represent the means and SEM for the qPCR (three biological replicates and three technical replicates) and UPLC (five biological replicates) experiments. Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test was performed to compare transgenic lines with the wild type. *P<0.05, **P<0.001, ***P<0.0001. ABA, abscisic acid; Car, carotenoids; Chl, chlorophyll; GA, gibberellins; L2, pJM36-2; L10, pJM37-10; L15, pJM37-15; LHC, light harvesting complex; MEP, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate; WT, wild type; Xan, xanthophylls.