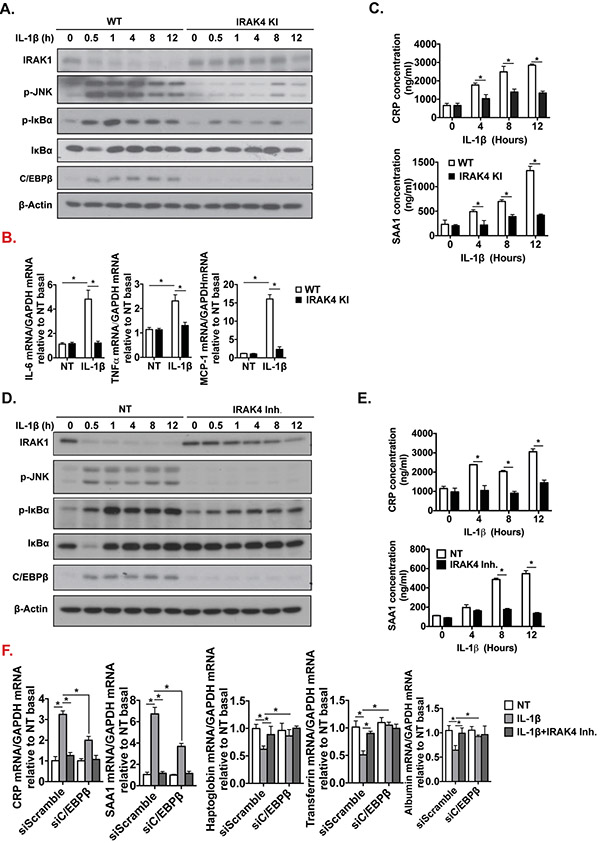
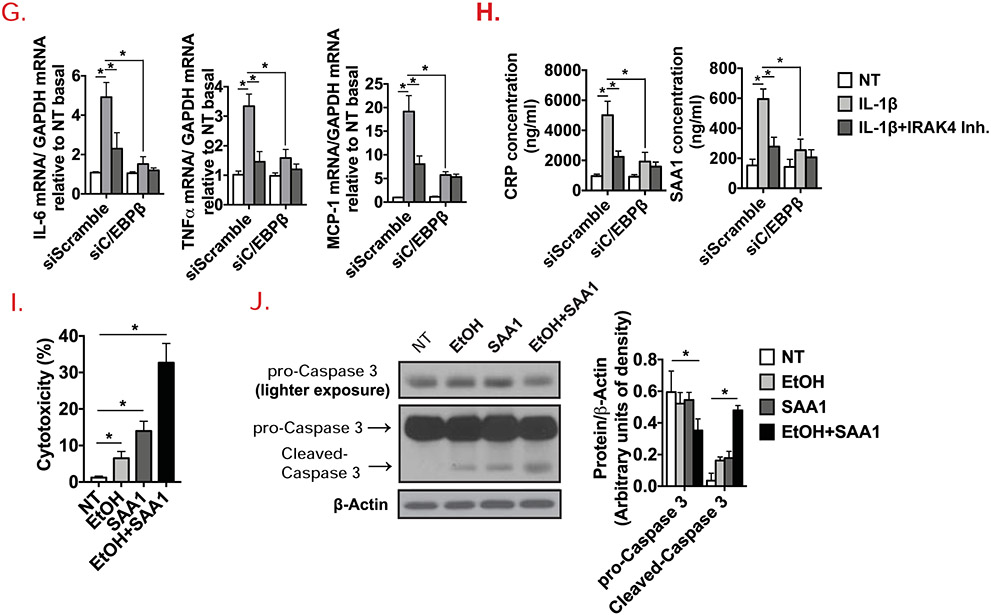
Figure 5. Hepatocyte-specific IRAK4 is associated with acute-phase protein release in response to IL-1β.
(A) Western blot analysis of IL-1β-treated whole cell lysates from cultured WT and IRAK4 KI primary hepatocytes, and (D) WT primary hepatocytes with or without IRAK4 inhibitor treatment. CRP and SAA1 concentrations were measured in culture media from WT and IRAK4 KI primary hepatocytes (C) or IRAK4 inhibitor treated WT primary hepatocytes (E) by ELISA. (B) Total mRNAs from WT and IRAK4 KI primary hepatocyte treated with or without IL-1β for 12 hours were subjected to RT-qPCR analysis. (F-G) Total mRNAs from AML12 cells with or without C/EBPβ knockdown with indicate treatments for 12 hours were subjected to RT-qPCR analysis. (H) CRP and SAA1 concentrations were measured by ELISA in Culture media from (F). (I) WT Primary hepatocytes were treated with EtOH (150 mM) for 20 hours, mouse recombinant SAA1 (5 μg/ml) or DMSO were then added for 8 hours. Cytotoxicity were assessed by MTS assay. (J) Western blot analysis of whole cell lysates from cultured primary hepatocytes from (I). Images were quantified by ImageJ software. The experiments were repeated for three times with similar results. Data represent mean ± SEM, *: p < 0.05. by Two- way ANOVA or Student’s t-test. IRAK4 Inh., IRAK1/4 inhibitor