Figure 6.
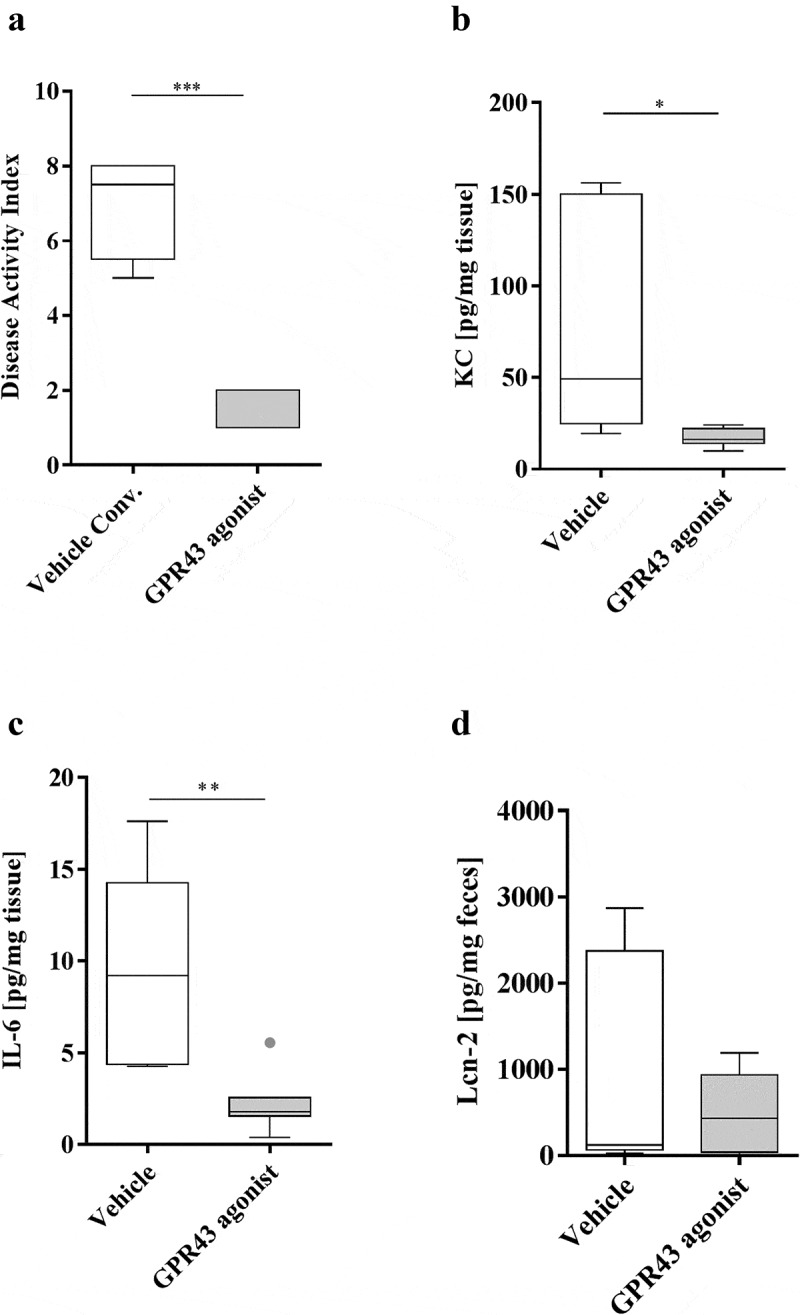
The GPR43 agonist decreases the severity of colitis in AIEC LF82-infected mice
CEABAC10 mice (n = 8 for each group) were pretreated with an antibiotic cocktail containing 500 mg/L metronidazole, 1 g/L streptomycin, 1 g/L neomycin and 1 g/L ampicillin. Mice were orally challenged for 7 days with 109 CFU of AIEC LF82 bacteria and with 5 mg/kg/day GPR43 agonist. Simultaneously, the drinking water of the mice was supplemented with 0.25% DSS. (a) Disease activity index (DAI) of AIEC LF82-exposed mice on day 10. (b,c) Secreted KC and IL-6 cytokines in colonic tissue culture supernatant. (d) Secreted lipocalin-2 (Lcn-2) in the feces of mice treated with the GPR43 agonist and of untreated mice. The results are presented as the median values. Statistical comparisons were carried out by normality testing using Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests, and a subsequent two-tailed Student’s test (b,c) or Mann–Whitney U-test (a–d) was performed (*p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001).
