Figure 1. RING E3 ligases ubiquitylate H2A at distinct sites on the nucleosome.
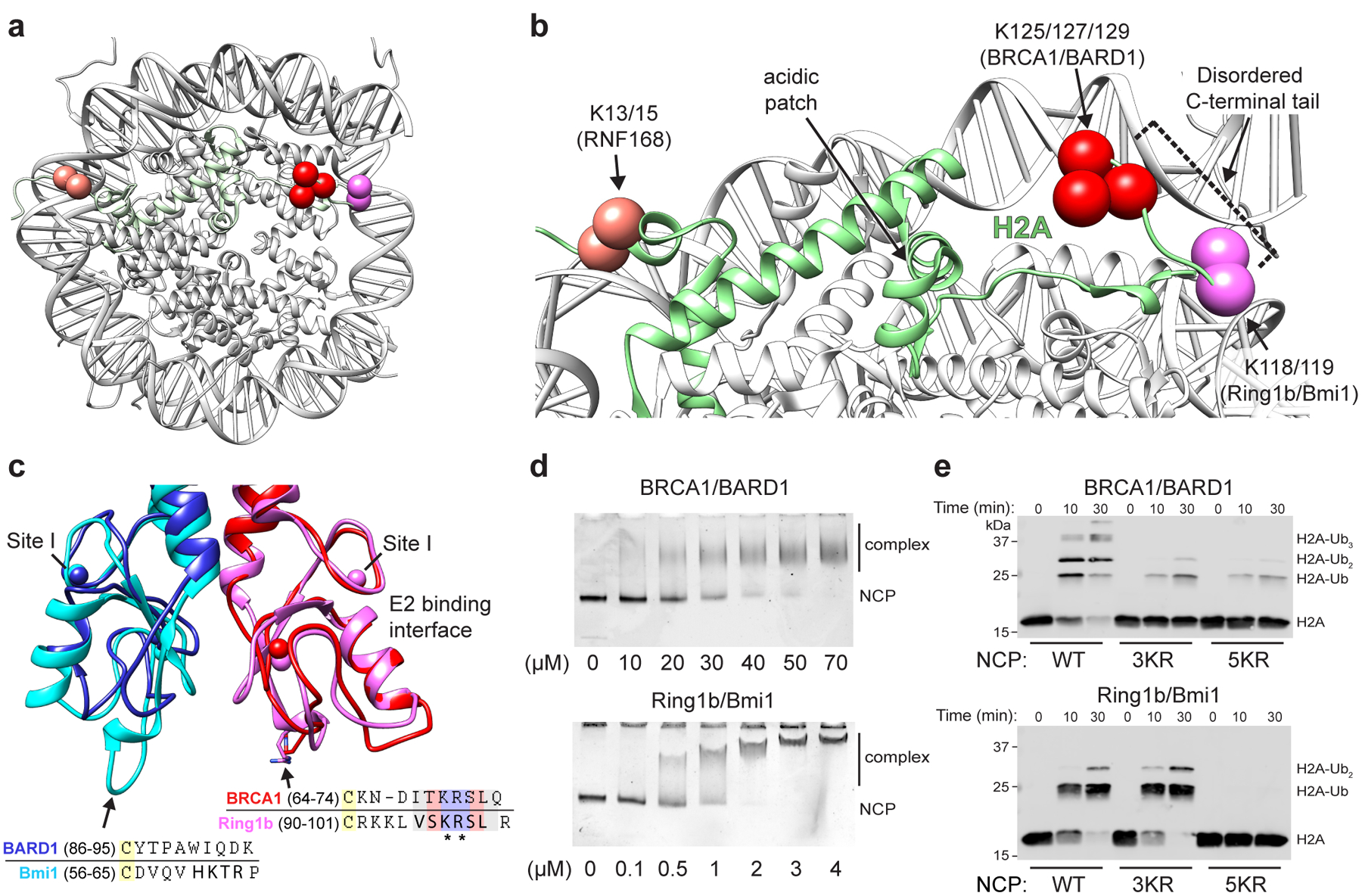
(a) Location of primary target lysine residues (Cαs, colored spheres) for BRCA1/BARD1 (K125/127/129, red) Ring1b/Bmi1 (K118/119, magenta), and RNF168 (K13/15, salmon) on one face of the nucleosome core particle (NCP; PDB: 1KX5). (b) Close-up of H2A (green) from panel a. The H2B αC helix is hidden for clarity. Residues past H2A Lys118 are disordered and generally not observed as density in X-ray or cryo-EM structures. (c) Structural and sequence alignment of BRCA1/BARD1 (PDB: 1JM7) and Ring1b/Bmi1 (PDB: 2CKL) RING domains with arrows pointing towards the nucleosome binding regions of Ring1b and Bmi1. Bolded residues in the sequence alignment are primary Ring1b and Bmi1 nucleosome binding loop residues. Asterisks denote arginine anchor motif residues. Yellow highlighted cysteine residues are nearest analogous Zn2+-coordinating residues. Zinc atoms are shown in structures as colored spheres (partially overlapping) with zinc site I labeled for each RING domain. (d) Native-gel electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) measuring BRCA1/BARD1 and Ring1b/Bmi1 RING heterodimer binding to NCPs. Concentration of RING binding partner (indicated below the gels) is different between E3s. Data are representative of n=2 (Ring1b/Bmi1) or n=3 (BRCA1/BARD1) independent binding experiments. (e) Nucleosome ubiquitylation assays (Western blot for VSV-G tag on H2A) using either BRCA1/BARD1 or Ring1b/Bmi1 RING heterodimers and wild-type (WT), H2A Lys125/127/129Arg (3KR), or H2A Lys118/119/125/127/129Arg (5KR) NCP substrates. Data in panel e are representative of n=2 independent experiments. Uncropped gel/blot images in panels d and e are available as source data.
