Figure 7.
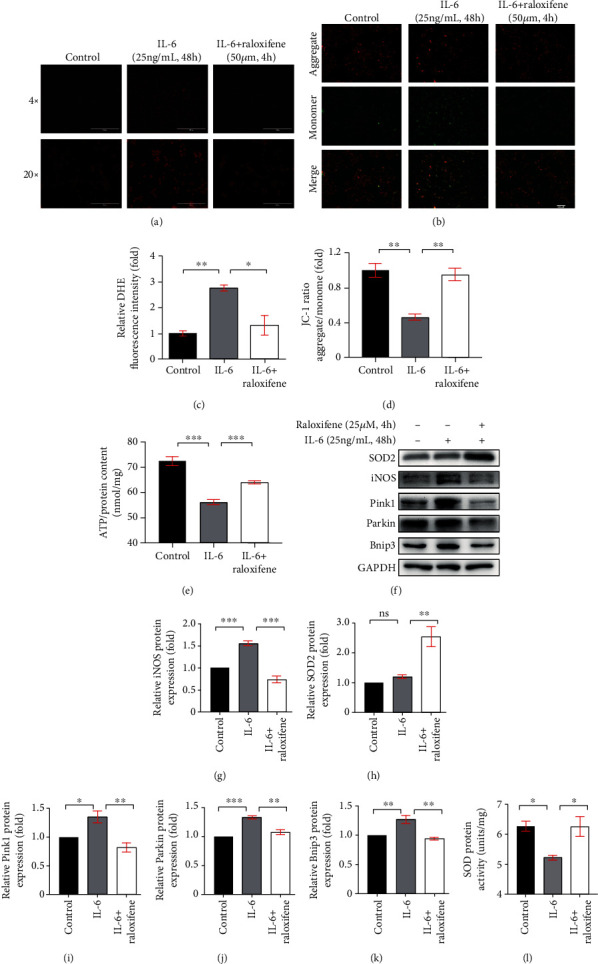
Raloxifene reduced oxidative stress and regulated mitophagy-related protein expression elicited by IL-6 in H9c2 myoblasts. (a, c) The DHE staining (a) showed that raloxifene alleviated reactive oxygen species production induced by IL-6 (scale bar: 1000 μm for 4x; 200 μm for 20x) and the bar graph (c) showing the mean DHE fluorescence intensity of nuclei in H9c2 myoblasts. (b, d) The JC-1 staining (b) showed that raloxifene reversed the decrease of mitochondrial membrane potential elicited by IL-6 (scale bar, 400 μm); red fluorescent (aggregate)/green fluorescent (monomer) ratio (D) was decreased with the IL-6 incubation and was reversed by raloxifene treatment. (e) The intracellular ATP content was decreased after the continuous incubation of IL-6 for 48 hours but was maintained after pretreating with raloxifene before IL-6 incubation. (f–k) Raloxifene increased the antioxidative protein SOD2 expression (h) and decreased the prooxidative protein iNOS expression (g) of H9c2 myoblasts incubated with IL-6. Meanwhile, raloxifene regulated the mitophagy-related protein of Pink1 (i), Parkin (j), and Bnip3 (k) to normal status. (l) The sustained IL-6 stimulation decreased the total intracellular SOD protein activity and was reversed by raloxifene treatment. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001, “ns” stands for “none significance”.
