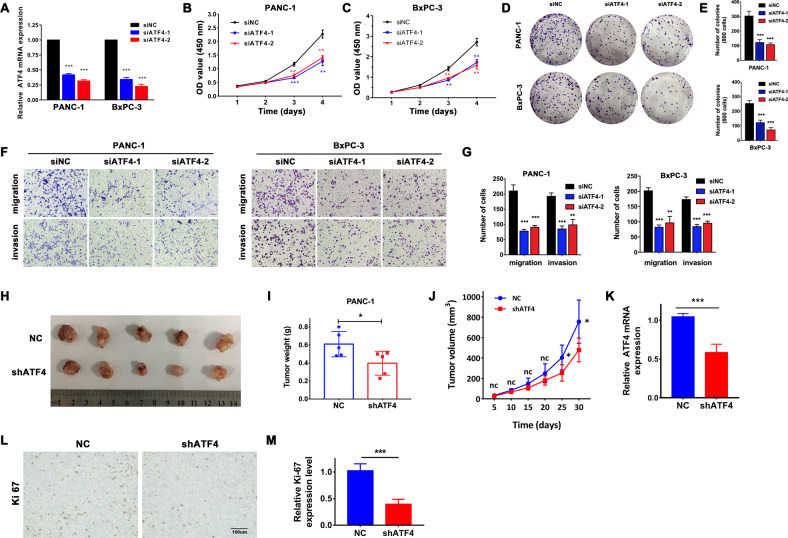
Fig. 2. Silencing ATF4 expression inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo.
A qRT-PCR assay was performed to detect the silencing effect of ATF4 siRNA in PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells. n = 3, ***p < 0.001. B, C CCK8 analysis showed the growth curve of PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells transfected with ATF siRNA. n = 3, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. D, E Plate colony formation assays showed that colony formation decreased in PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells with ATF4 silencing. n = 3, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. F, G. Transwell assays showed the fractions of migrated and invaded PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells. Silencing ATF4 expression decreased the migration of invaded pancreatic cancer cells. n = 3, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. H Image of harvested tumors from PANC-1 cells with stable ATF4 knockdown or mock cells subcutaneously transplanted into the bilateral hind legs of nude mice. I The tumor weights are shown as the mean ± SD, n = 5. *p < 0.05. J The tumor growth curve. The points and bars represent the mean ± SD. n = 5, ns not significantly different. *p < 0.05. K qRT-PCR assay analyzed the mRNA expression level of ATF4 in tumor tissues from shATF4 PANC-1 cells compared with mock cells. n = 5, ***p < 0.001. L, M IHC staining showed that the positive expression rate of Ki67 was lower in tumor samples from shATF4 PANC-1 cells than in mock cells. n = 5, ***p < 0.001.