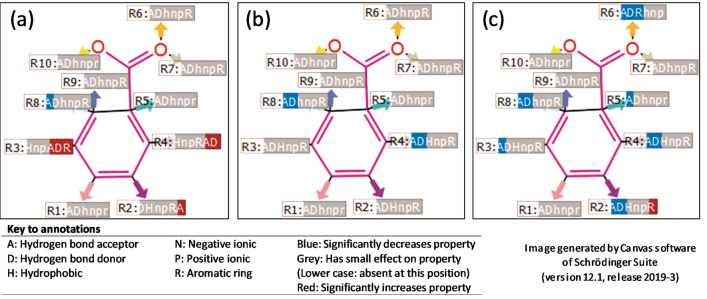
Figure 6.
Pharma rational quantitative structure–activity relationship models indicating the R-groups most likely responsible for the (a) tyrosinase activity, (b) tyrosinase structure (PBD: 2Y9X) docking score properties and (c) tyrosinase related protein 1 structure (PBD: 5M8P) docking score properties. According to the six pharmacophore elements analysed, the substituent groups at the R2 position (hydrogen bond acceptor), R3 (hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor and aromatic ring) and R4 (hydrogen bond acceptor and hydrogen bond donor) had a significant increase on the tyrosinase activity. The substituent groups at the R8 position (hydrogen bond acceptor) had a significant decreasing effect on the activity. The substituent groups at the R4 position (hydrogen bond acceptor and hydrogen bond donor) and R8 position (hydrogen bond acceptor and hydrogen bond donor) had a significant decreasing effect on the tyrosinase structure docking score properties. The substituent groups at the R2 position (hydrogen bond acceptor and hydrogen bond donors), R3 (hydrogen bond acceptor), R4 (hydrogen bond acceptor and hydrogen bond donors), R5 (hydrogen bond acceptor), R6 (hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donors and aromatic ring), and R8 (hydrogen bond acceptor and hydrogen bond donor) had a significant decreasing effect on the tyrosinase-related protein 1 structure docking score properties. In contrast, the substituent groups at R2 (aromatic ring) had a significant increasing effect (https://www.schrodinger.com/canvas; version 4.1.013, release 2019-3).