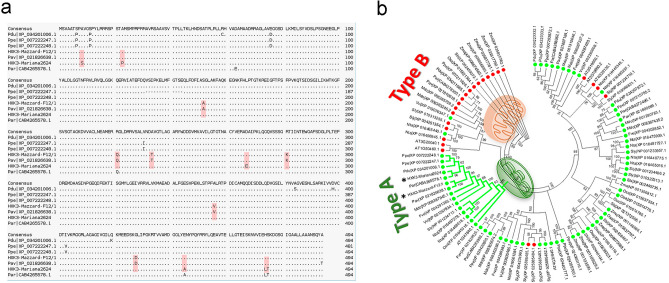
Figure 2.
Identification of two putative Prunus HXK3 enzymes. (a) Comparison of predicted amino acid sequences of ‘M.2624’ HXK3 and ‘M.F12/1’ HXK3 with homologs from Prunus species. Differences at the amino acids level between proteins are enclosed in red squares. (b) Phylogenetic relationship among HXK proteins. The phylogram was generated with the MEGA 6.0 program from the multiple alignments of the deduced amino acid sequences from Prunus HXK3 and other angiosperm HXK proteins. Bootstrap values from 1000 replicates were used to assess the robustness of the tree. Green (chloroplast/plastid) and red (mitochondria) dots indicate the putative subcellular localization of HXK proteins (Plant-mSubP, http://bioinfo.usu.edu/Plant-mSubP/). The types of plant HXK are indicated. The positions of ‘M.2624’ and ‘F.12/1’ HXKs are indicated by asterisks. Gene identification are: AT, Arabidopsis thaliana; Fve, Fragaria vesca subsp. vesca; Mdo, Malus domestica; Nta, Nicotiana tabacum; Osa, Oryza sativa Japonica Group; Ppa, Physcomitrella patens; Par, Prunus armeniaca; Pav, Prunus avium; Pdu, Prunus dulcis; Ppe, Prunus persica; Sly, Solanum lycopersicum; Sbi, Sorghum bicolor; Vvi, Vitis vinifera; Zma, Zea mays.