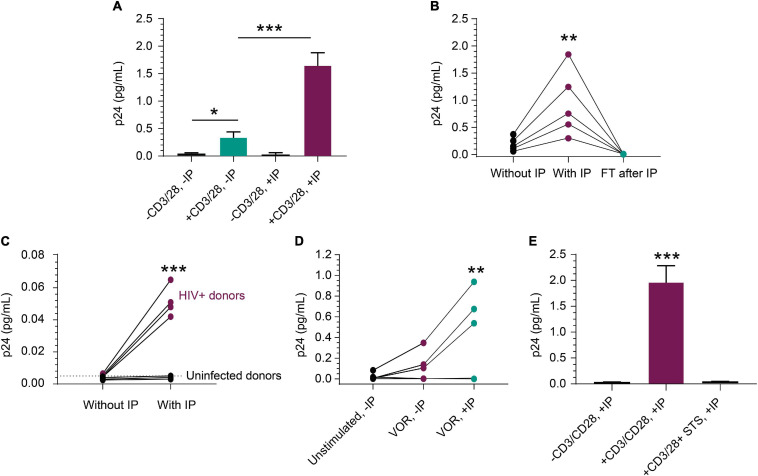
FIGURE 3.
Detection of p24 from HIV+, ART-suppressed peripheral blood CD4+ T cells. (A) p24 production was induced in CD4+ T cells following a 3-day stimulation with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads (n = 3 independent experiments, p < 0.05). p24 was enriched 5-fold with a 5-fold volume reduction after IP in treated group (n = 3, p < 0.001), but not in unstimulated group. (B) From samples that respond well to stimulus, p24 was enriched proportionally to volume reduction in five inducible donors (p < 0.01), and no detectable p24 was observed in their flow through after IP. (C) From samples that do not show robust p24 production after stimulation, IP enrichment was able to demonstrate that p24 is indeed produced but was not at the limit of detection without enrichment. Even with enrichment and bead stimulation, p24 was not detected from HIV-negative CD4+ T cells and shows significant difference (p < 0.001) between HIV+ and uninfected donors after IP. (D) p24 protein was detected following a 3-day treatment with 1 μM VOR in three of the five donors’ CD4+ T cells (4 × 106 cells/condition). The signal was enriched significantly after p24 IP with 4-fold cell lysate volume reduction (p < 0.01). No p24 was detected from unstimulated cells. This opens the door for studying even weak LRAs’ effects using donor-derived cells. (E) Mimicking applications with kill-focused assays, p24 was not detected when including 1 μM staurosporine along with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 bead stimulation for those three inducible donors (p < 0.001). See Materials and Methods for statistical analysis.