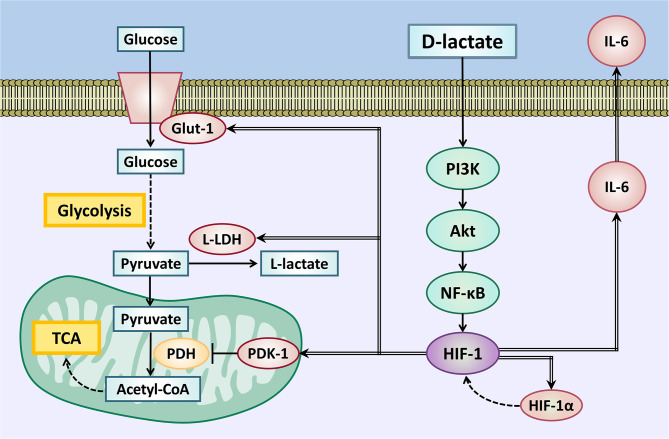
Figure 9.
Metabolic reprogramming supports the inflammatory response induced by D-lactate in bFLS. D-Lactate induces the PI3K/Akt pathway activation and downstream activation of NF-κB and HIF-1. Through this signaling pathway, D-lactate induces the gene expression of IL-6, with the pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in the synovial inflammatory response. HIF-1 activation also increases the expression of the Glut-1 transporter, which increases glucose uptake for use in glycolysis. Glycolysis is also favored by the HIF-1-dependent overexpression of L-LDH, which oxidizes pyruvate to L-lactate. In addition, an increased PDK-1 expression blocks the mitochondrial utilization of pyruvate through the TCA cycle, contributing to the glycolytic fate of glucose. Overexpression of the HIF-1α subunit would favor the accumulation of HIF-1 heterodimers, maintaining glycolytic metabolic reprogramming. IL-6, interleukin 6; Glut-1, solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter) member 1; L-LDH, L-lactate dehydrogenase; PDK-1, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1; HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; PI3K, phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase; Akt, protein kinase B; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; HIF-1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1.