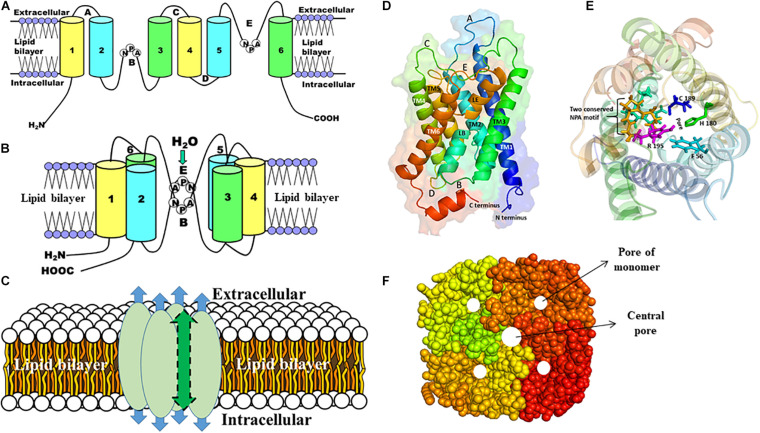
FIGURE 2.
The structure of AQP monomer and homotetramers. A schematic representation of the general structures of AQP is shown (A–C). (A) Each AQP monomer has six transmembrane domains (1–6) spanning the plasma membrane, which are connected with five loops (A–E). (B) Two conserved NPA motifs in loops B and E are juxtaposed oppositely to form the channel through which molecules are passed. (C) Each AQP monomer contains independent pore (shown as blue arrow) and the monomers are assembled as tetramers to form a central pore (shown as green arrow). (D) Side view of the structure of the human AQP1 monomer, which shows six transmembrane α-helices (TM1-6) including pseudo TM (LE and LB) that are connected with five different loops (A–E). (E) The top view of the human AQP1 is shown. The residues (F56, H180, C189, and Arg195) in the ar/R constriction and two NPA motifs (yellow and cyan) are shown in sticks. (F) The top view of the AQP homotetramers with filled amino acid residues is shown. The pore of each monomer and the central pore of the homotetramers are shown as white circles.