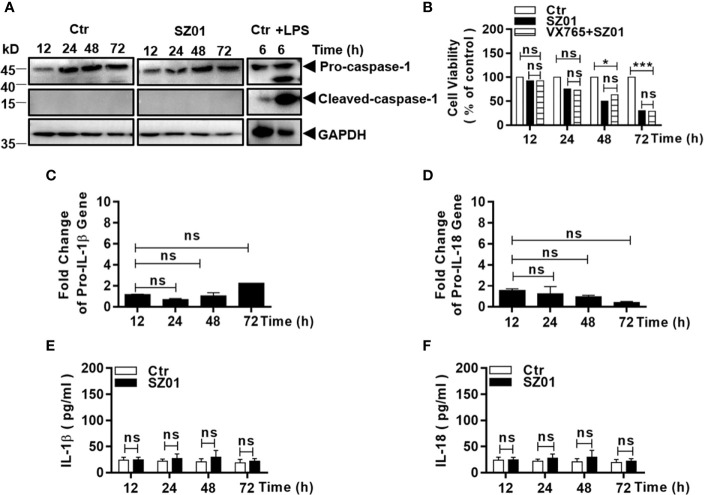
Figure 4.
ZIKV did not activate pyroptosis in human astrocytes. (A) U251 cells were infected with 1 MOI of ZIKV and cell lysates were prepared at various time points p.i. and subjected to western blot analyses with specific antibodies (1:1000) as indicated. Monocytic THP-1 cells, were treated with or without lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 1μg/ml), and the lysates analyzed as a positive control for pyroptosis. (B) Cell viability was analyzed in pre-treated U251 cells infected with 1 MOI of ZIKV. The cells were pre-treated with or without VX765, an inhibitor of pro-caspase-1, prior to ZIKV infection and analyzed for viability at various times p.i. with the MTT assay. The experiments were repeated at least three times (ns p>0.05; *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001). (C, D) No transcriptional changes occurred to pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 in infected cells. Total RNA was prepared from the U251 cells infected with ZIKV to measure mRNA transcript copies using quantitative real time PCR with specific primers for genes of IL-1β (C) and IL-18 (D), respectively. (E, F) No change in secreted IL-1β and IL-18 levels in the cell cultures after ZIKV infection. Culture media was collected at various time points p.i. for measurement of IL-1β and IL-18 by ELISA. Each data point represents the mean values from triplicate cultures performed at least three times (ns p > 0.05).