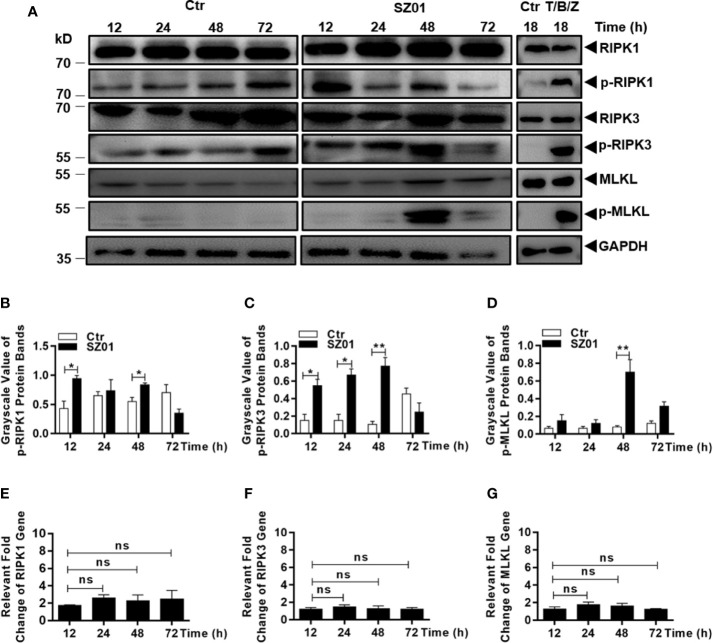
Figure 5.
Necroptosis was induced by ZIKV-infected human astrocytes. (A) Increased phosphorylation of necroptosis-associated proteins was detected in ZIKV-infected cells. Cell lysates were prepared at various time points p.i. and subjected to SDS-PAGE and western blot analyses with specific antibodies (1:1000) for the proteins, either non-phosphorylated or phosphorylated, as indicated. The efficacies of the antibodies were confirmed with the lysates prepared from HT-29 cells treated with or without TNF-α (20 ng/ml), BV-6 (100 nM) and Z-VAD-FMK (20 µM) for induction of necroptosis. (B–D) Quantitative analyses of the gray scale values of the phosphorylated RIPK1 (B), RIPK3 (C), and MLKL (D) between ZIKV infected and non-infected cells at various time points p.i. (E–G). Relative level of each protein was normalized to GAPDH at indicated time points. No changes of RIPK1, RIPK3 and MLKL at the transcriptional level in U251 cells after infection with ZIKV. Total RNA was prepared from infected cells at several time points p.i. for measuring mRNA transcript copy numbers by real time PCR with specific primers for RIPK1 (E), RIPK3 (F), and MLKL (G), respectively. The experiments were repeated three times and the data are shown as means ± SEM (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ns p > 0.05).