Fig. 1.
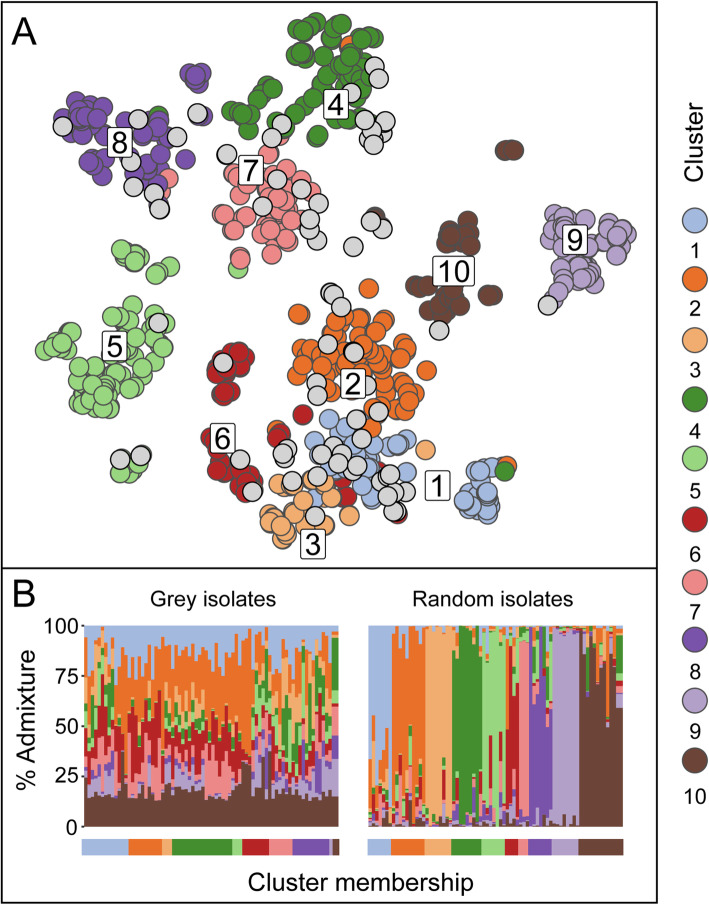
Clustering among global A1 isolates. a Clustering of 973 E. faecium group A1 isolates based on the presence or absence of genes within the pan-genome identified using Panaroo. Labelled clusters are represented on a reduced dimensionality 2-D grid with member isolates coloured as shown in the legend. At a core-genome SNP level isolates within the same cluster are expected to share the same ancestry across the majority of their genomes. Using ChromoPainter, substantial core-genome admixture was detected in the 78 grey-shaded isolates, resulting in their exclusion from the designated pan-genome clusters. b The levels of admixture of the aforementioned 78 grey-shaded isolates in a (left) are contrasted with estimated admixture of 78 randomly chosen isolates from the remaining 895 isolates. The x-axis label shows the initial cluster assignment based on the pan-genome with the y-axis bars representing co-ancestry signals originating from other clusters, using the same colours as in a