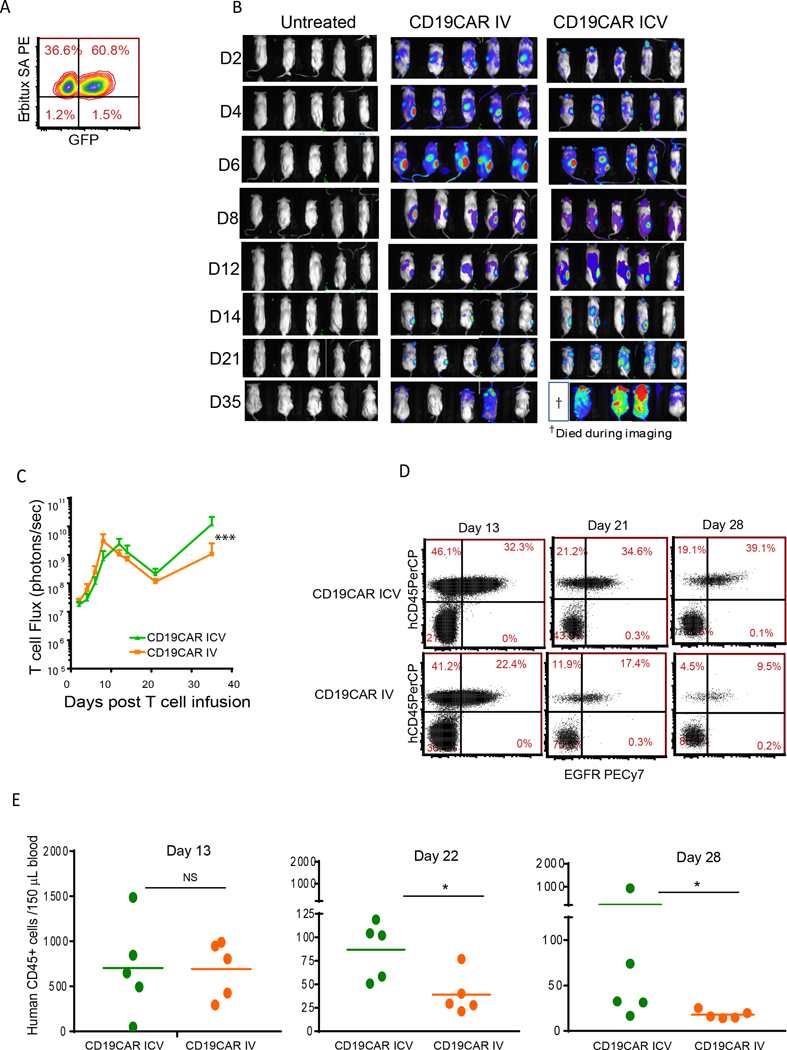
Figure 4. ICV-infused CAR T cells exhibit similar trafficking, but superior proliferation and persistence potential when compared with IV-delivered CAR T cells.
(A) CD19-CAR T cells were transduced with EGFP-ffluc and expanded in vitro. NSG mice were implanted subcutaneously with Daudi lymphoma in the right flank. Nineteen days after tumor engraftment, 2×106 EGFP+ffluc+ CAR T cells were administered ICV or IV and CAR T cell proliferation was determined by measuring bioluminescence by live imaging every other day (B-C). The same scale was used for each time point. (D-E) Blood was collected at different time points post-CAR T cell infusion, and T cell (human CD45+) and CAR+ T cell (EGFR+) levels were detected by flow cytometry. Mean ±SDs from 5 mice per group are presented. Significance was determined with the Mann-Whitney test; *P<0.05; ***P<0.001. Experiments were repeated twice and representative data are presented.