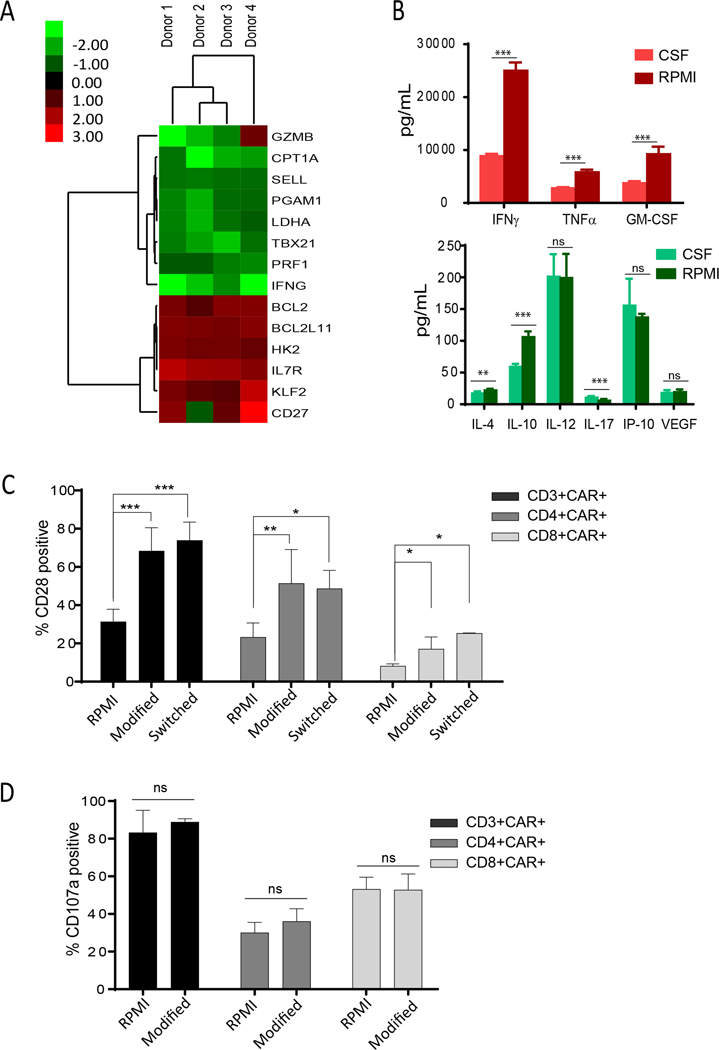
Figure 5. CSF conditions CAR T cells for enhanced memory and reduced exhaustion.
(A) CD19-CAR T cells were cultured in RPMI or human CSF for 48 hours and subjected to RT-PCR array analysis. Fold-changes of genes in CSF over RPMI of >1.3 are shown. N=4 donors. (B) CAR T cells cultured in CSF or RPMI for 48 hours were stimulated overnight with Daudi lymphoma cells. Cytokines released into the supernatant were measured with cytometric bead array using the Bio-Plex Human Cytokine 17-Plex Panel. Mean ±SDs from 6 replicates are presented. CSF and RPMI (logarithm transformation) were compared by Student’s t test; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. (C) CAR T cells were activated, transduced, and expanded for 13 days in modified RPMI (60mg/dL glucose; 2.8 mEq/L potassium) or in regular RPMI (200 mg/dL glucose; 5.3 mEq/L potassium). CAR T cells cultured in modified RPMI were subsequently cultured in regular RPMI (Switched) for 14 days. Percentages (mean ±SD) of CD28 positive cells in CAR-gated populations from N=4 different human donors are presented. Linear mixed models were used to compare the three conditions based on repeated measures from the same donor; *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. (D) CAR T cells were cultured in modified or regular RPMI, stimulated with Daudi cells for 6 hours, and assessed for degranulation. Percentages (mean ±SD) of CD107+ cells in CAR gated populations from N=4 different human donors are presented.