Figure 5.
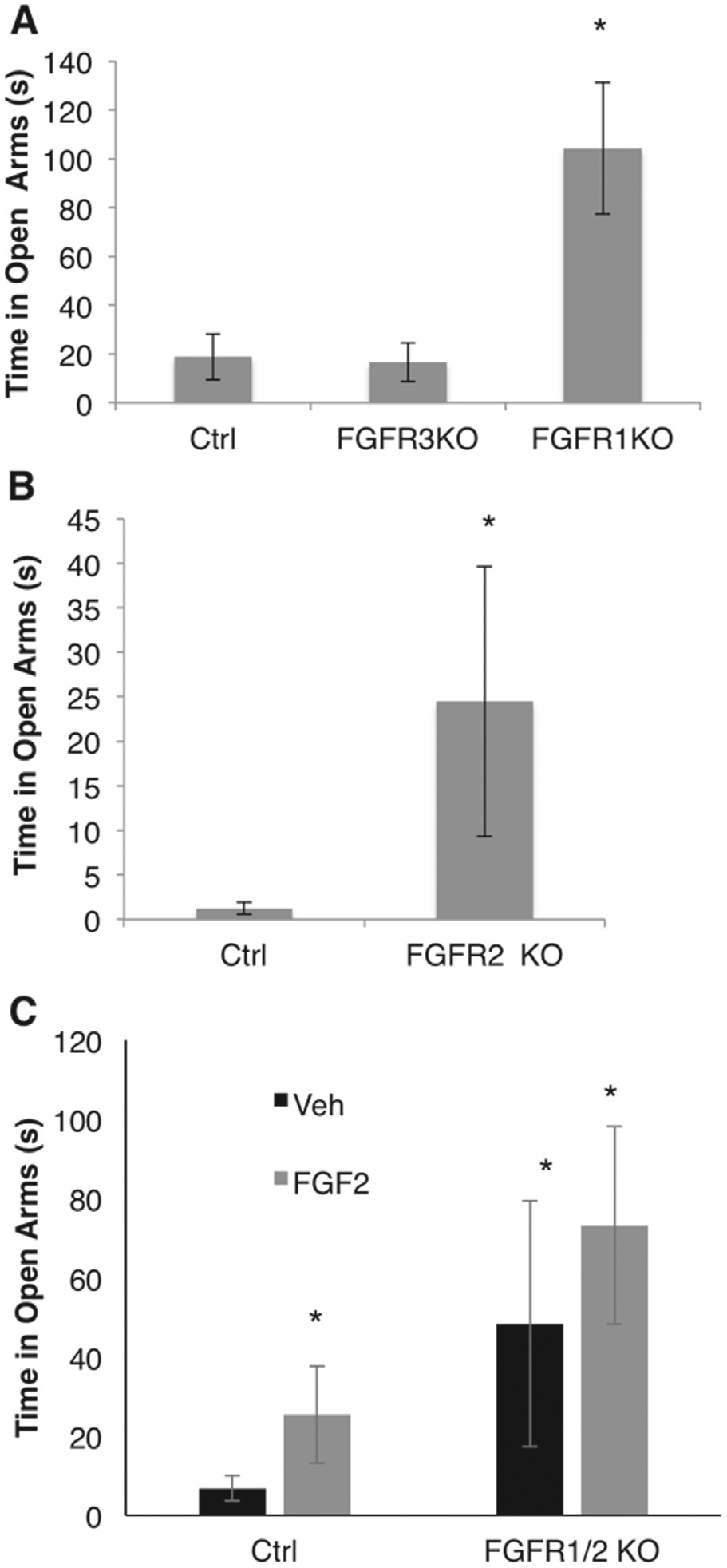
The role of fibroblast growth factor receptor (Fgfr)1, 2, and 3 in anxiety behavior. Panel (A) shows time on the open arms in control (Ctrl) (cre-negative or wild type), Fgfr3 constitutive knockout (FGFR3 KO), and Fgfr1 conditional KO mice (FGFR1 KO) driven by Emx1-cre (Ctrl, n 5 12; Fgfr3 KO, n = 13; Fgfr1 KO, n = 8). Panel (B) shows time on the open arms of the elevated plus maze in Ctrl (cre-negative) and Fgfr2 conditional KO mice (FGFR2 KO) driven by the hGFAP-cre line (Ctrl, n = 9; Fgfr2 KO, n = 9). Panel (C) shows time on the open arms in Ctrl (cre-negative) and FGFR1/2 conditional KO mice driven by Emx1-cre in response to vehicle (Veh) or Fgfr2 administration (Ctrl, Veh, n = 8; Fgfr1/2 KO, Veh, n = 6; Ctrl, FGF2, n = 10; Fgfr1/2 KO, FGF2, n = 6). *Denotes significant differences from Ctrl. Error bars denote SEM.
