Figure 5.
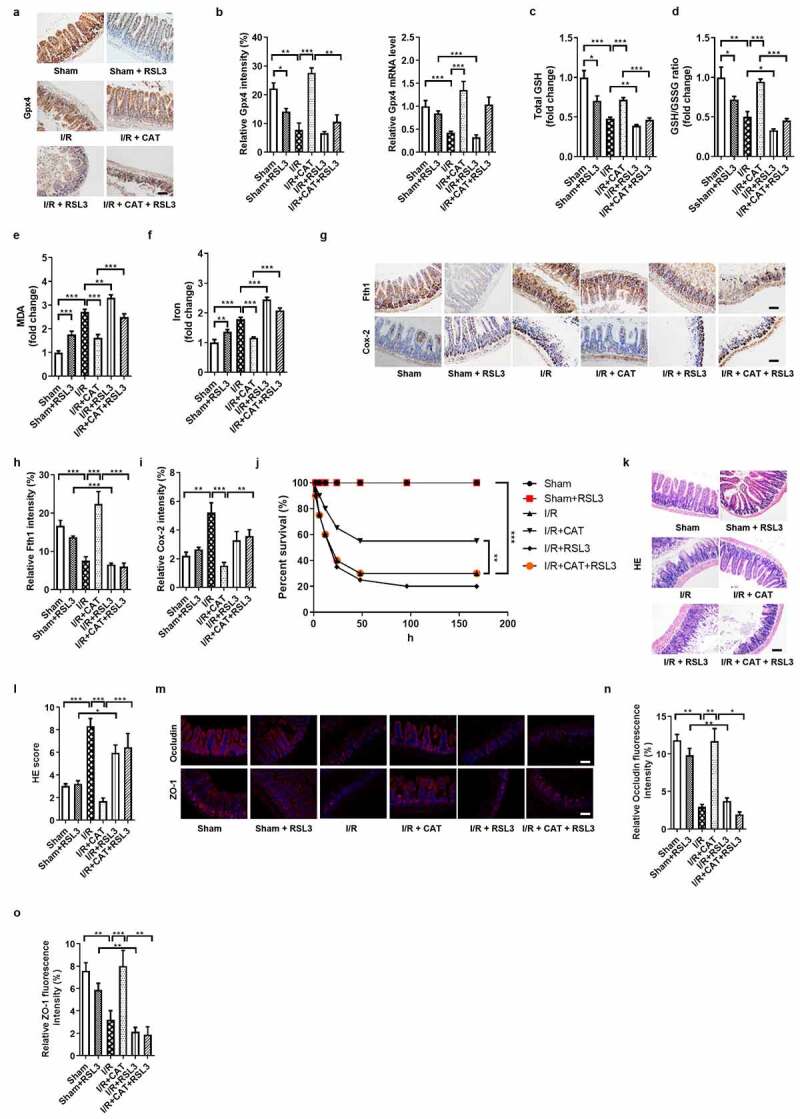
CAT inhibits ferroptosis-dependent intestinal I/R injury by promoting Gpx4 expression. (a) The protein levels of glutathione Gpx4, scale bar is 100 μm. (b) Relative quantitative statistics of Gpx4 protein expression and relative Gpx4 mRNA level in the intestinal tissue. (c-d) The total glutathione (GSH) and GSH/GSSG levels in the intestinal tissue. (e-f) Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Fe2+ levels in the intestinal tissue. (g) The protein levels of Fth1 and Cox-2, scale bar is 100 μm. (h-i) Relative quantitative statistics of Fth1 and Cox-2 protein expression. (j) 7-day survival rate of mice after intestinal I/R, n = 20. (k-l) HE staining of small intestine tissue and Chiu’s pathology score. scale bar is 100 μm. (m) The relative protein levels of the intestinal barrier tight junction Occludin and ZO-1, scale bar is 100 μm. (n-o) Relative fluorescence quantitative statistics of Occludin and ZO-1 protein expression. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM. n = 8. * p < .05, ** p < .01, *** p < .001 by one-way ANOVA (Tukey’s test)
