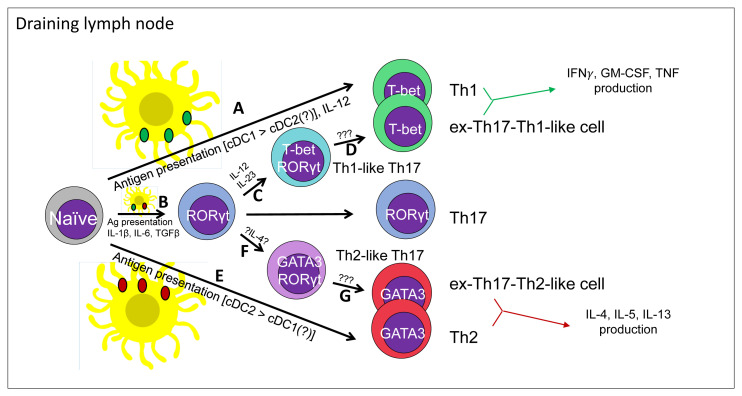
Figure 1. Contributions of dendritic cell subsets in the initiation of classical and alternative differentiation pathways for the generation of Th1 and Th2 cells in vivo.
Presented here is our updated view of the Th1/Th2 T effector decision in vivo. In response to an in situ immunological insult, local antigen-presenting dendritic cells acquire Ag and home to the nearest draining lymph node to present Ags. In the case of a pro-Th1 insult, such as a bacterial infection, bacterial Ag-laden dendritic cells can present bacterial Ags to naïve T cells and produce IL-12 in order to help generate bacterial Ag-specific Th1 cells (A). In parallel, some bacterial PAMPs can trigger Ag-laden dendritic cells to produce pro-Th17 cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6, and TGFβ (B). Bacterial Ag-specific Th17 cells can subsequently respond to IL-12 and/or IL-23 in order to generate T-bet+ Th1-like Th17 cells (C) and ex-Th17-Th1-like cells (D) via unclear mechanisms. In contrast to a pro-Th1 insult, allergen exposure or a helminth infection is able to elicit a Th2 Ag-specific T cell response. In this scenario, helminth- or allergen-Ag-bearing dendritic cells home to the nearest draining lymph node, where they may select for Ag-specific naïve T cells to generate an Ag-specific Th2 cell response (E). In parallel, some helminth- or allergen-Ag-laden dendritic cells may instead help to generate Th17 cells, which may subsequently give rise to GATA3+ Th2-like Th17 cells (F) and ex-Th17-Th2-like cells (G). Ag, antigen; cDC, conventional dendritic cell; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; TGFβ, transforming growth factor beta; Th1, type 1 T helper; Th2, type 2 T helper; Th17, interleukin-17-producing T helper; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.