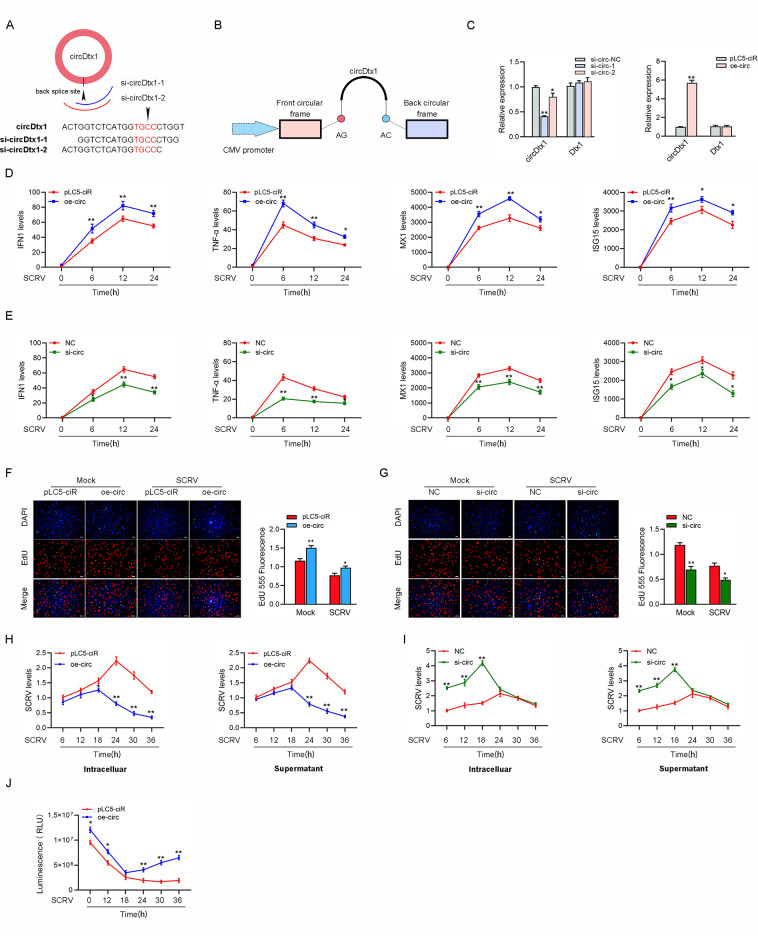
Fig 2. circDtx1 promotes the antiviral innate immunity.
(A and B) The schematic diagram of siRNAs (A) and oe-circ structure (B) qPCR analysis of circDtx1 and linear Dtx1 mRNA in MIC cells treated with siRNAs. (C) qPCR analysis of circDtx1 and linear Dtx1 mRNA in MKC cells stably overexpressing circDtx1. (D and E) qPCR assays were performed to determine the expression levels of IFN1, TNF-α, MX1, and ISG15 in MKC cells transfected with overexpression plasmid (oe-circ) or control vector (pLC5-ciR) (D) and MIC cells transfected with (si-circDtx1-1) si-circ or NC (E). (F and G) Cell proliferation was assessed by EdU assays in MKC cells transfected with oe-circ or pLC5-ciR vector after SCRV infected 24 h (F) and MIC cells transfected with si-circ or NC after SCRV infected 18 h (G). (H and I) circDtx1 suppresses SCRV replication. MKC cells transfected with pLC5-ciR vector or oe-circ plasmid (H) and MIC were transfected with NC or si-circ (I) for 24 h, respectively, then infected with SCRV at different time. The qPCR analysis was conducted for intracellular and supernatant SCRV RNA expression. (J) Effect of circDtx1 on cell viability after SCRV infection. MIC cells were transfected with pLC5-ciR vector or oe-circ for 24 h, then treated with SCRV for different times. Cell viability assays were measured. All data represented the mean ± SD from three independent triplicated experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.