Fig. 3.
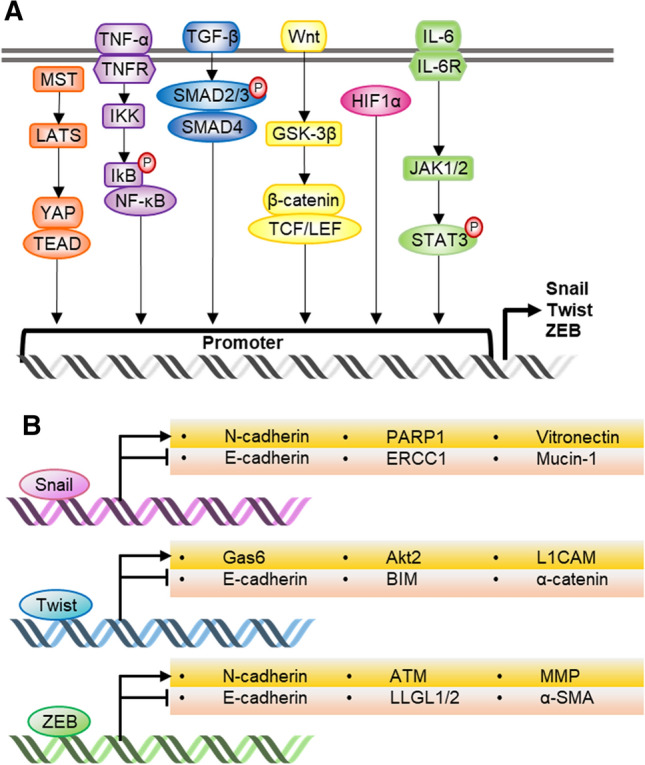
Key intracellular pathways and transcriptional target genes of EMT-TFs. a Several intracellular pathways induce transcription of EMT-TFs by binding to their promoter regions. b EMT-TFs regulate the expression of essential genes for EMT and drug-resistant related genes. NF-κB nuclear factor-κB, IKK IκB kinase, TNF-α tumor necrosis factor- α, TNFR tumor necrosis factor receptor, TNF-β transforming growth factor beta, GSK-3β glycogen synthase kinase-3β, TCF/LEF T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor, HIF1α hypoxia-inducible factor 1 α, IL-6 interleukin-6, JAK1/2 Janus kinase 1/2, STAT3 signal transducers and activators of transcription 3, PARP1 poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, ERCC1 excision repair cross-complementing group 1, GAS6 growth arrest-specific 6, L1CAM L1 cell adhesion molecule, BIM Bcl-2-like protein 11, ZO-1 zonula occludens-1, ATM ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, LLGL1/2 lethal giant larvae protein homolog 1/2, α-SMA α-smooth muscle actin
