Figure 4. Genomic variation in MYH7 enhancer regions.
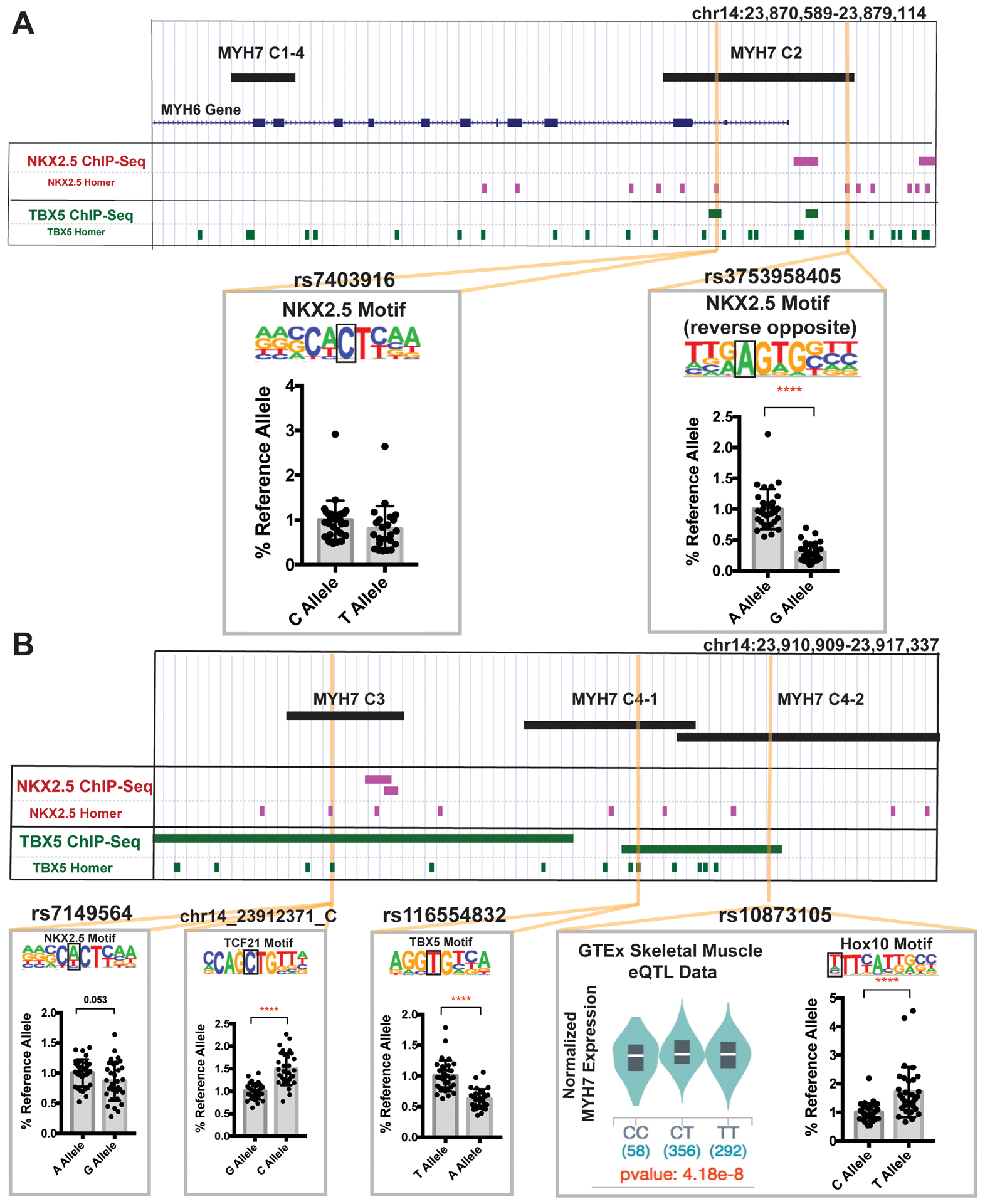
A. We queried the human genetic variation database gnomAD for naturally occurring human sequence variants in MYH7 enhancers. We selected variants overlapping cardiac transcription factor binding motifs, and/or correlating with MYH7 expression in the GTEx eQTL dataset. rs7403916 and rs373958405 fall within MYH7 C2 and disrupt NKX2.5 motifs. These variants were evaluated for reporter activity in IPSC-CMs and rs373958405 demonstrated reduced activity compared to the reference allele, indicating this variant may reduce expression by disrupting the enhancer activity of MYH7-C2. B. MYH7-C3 contains rs7149564 and chr14_23912371_C. rs7149564 disrupts an NKX2.5 motif and produced a trending reduction in activity in IPSC-CMs. chr14_23912371_C generates a TCF21 motif and produced an increased IPSC-CM luciferase signal. MYH7-C4 contains rs116554832 and rs10873105. rs116554832 disrupts a TBX5 motif and reduced activity in IPSC-CMs. rs10873105 is correlated with MYH7 expression in GTEx skeletal muscle data and creates a Hox10 motif. This variant generated increased activity in IPSC-CMs. These data indicate that sequence variants in transcription factor binding sites within enhancer regions can alter enhancer function and potentially affect MYH7 gene expression. All data shown as mean ± SD. Data was derived from an average of 30 different assays per condition, from across least 3 separate differentiations. Significance determined by unpaired t-test. ****<0.0001.
