Figure 7. Correlation of MYH6/7 rs875908 EMV with MYH7 mRNA cardiac expression and longitudinal shift in left ventricular dimensions over time in human cardiomyopathy patients.
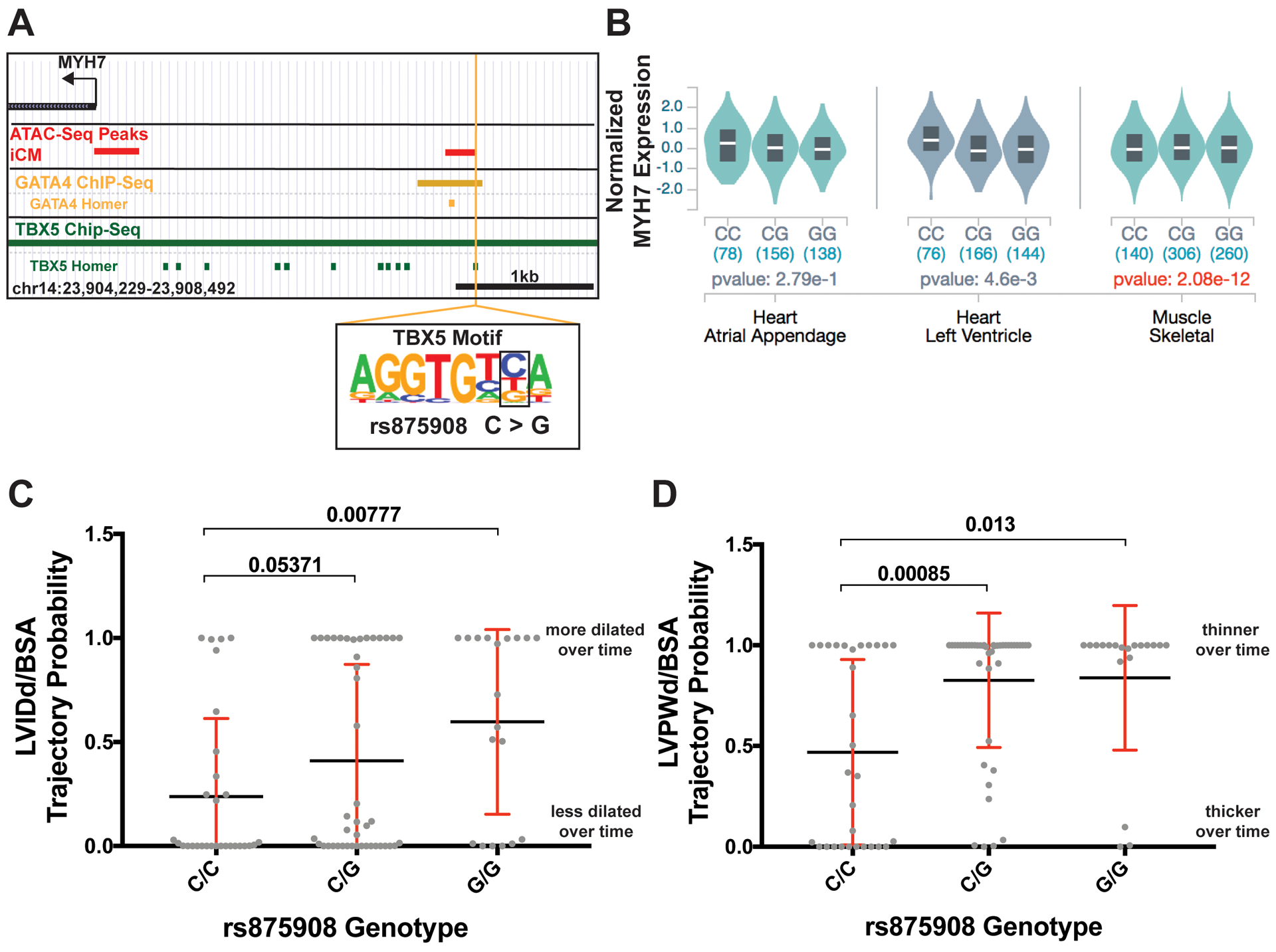
A. The location of the MYH6/7 regulatory variant is shown; it is bound by both GATA4 and TBX5 signals. The variant disrupts a site within the TBX5 transcription factor motif. B. eQTL data from the GTEx project shows that the variant genotype correlates with MYH7 expression across multiple striated muscle samples; the larger number of skeletal muscle samples yields genome wide significance in expression levels. C. Association of variant status with LVIDd/BSA over time in cardiomyopathy patients whose data was derived from the electronic data warehouse from Northwestern Medicine. D. Association of variant genotype with LVPWd/BSA over time in in cardiomyopathy cases. These data indicate that rs875908 associated with changes of left ventricular morphology including a more dilated left ventricle and thinner posterior wall. Significance determined using a linear regression model corrected for genetic ancestry and sex. LVIDd/BSA, left ventricular internal diameter during diastole corrected for body surface area. LVPWd/BSA, left ventricular posterior wall thickness during diastole corrected for body surface area.
