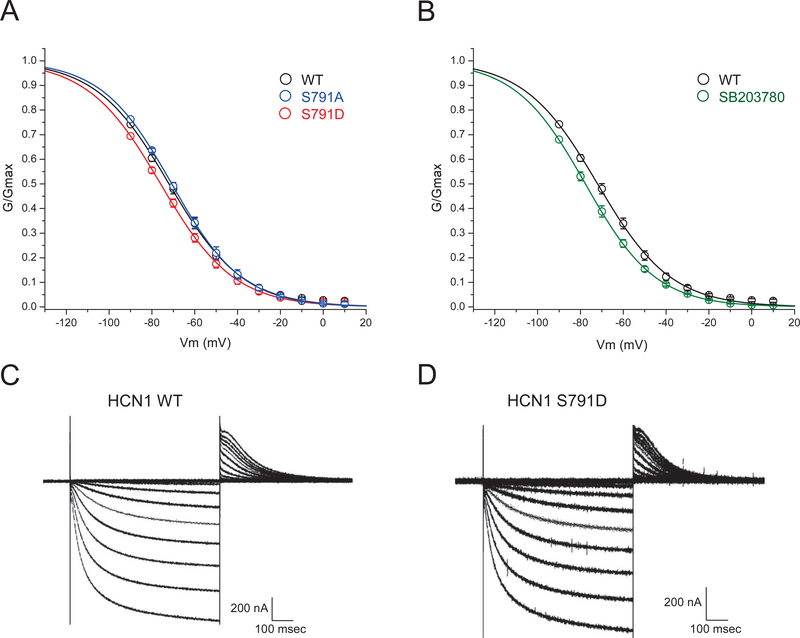
Figure 6.
Phosphomimetic mutation of S791 (S791D) negatively shifts HCN1 voltage-dependent activation. (A) Conductance/voltage (G/V) plots of WT HCN1, HCN1 with phosphomimetic mutation S791D, and HCN1 with phosphoablative mutation S791A are shown. Phosphomimetic mutation at S791 (S791D) produces an ~4 mV hyperpolarizing shift in HCN1 voltage-dependent activation, while ablation of phosphorylation with S791A mutation produces HCN1 activation that resembles WT. (B) Oocytes pretreated with the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203780 (20 μM) exhibit negatively shifted voltage-dependent activation compared to WT. (C) Example WT HCN1 currents evoked by voltage steps from 10 mV to −120 mV, with tail currents measured at 0 mV. (D) Example HCN1-S791D currents evoked by identical voltage steps.