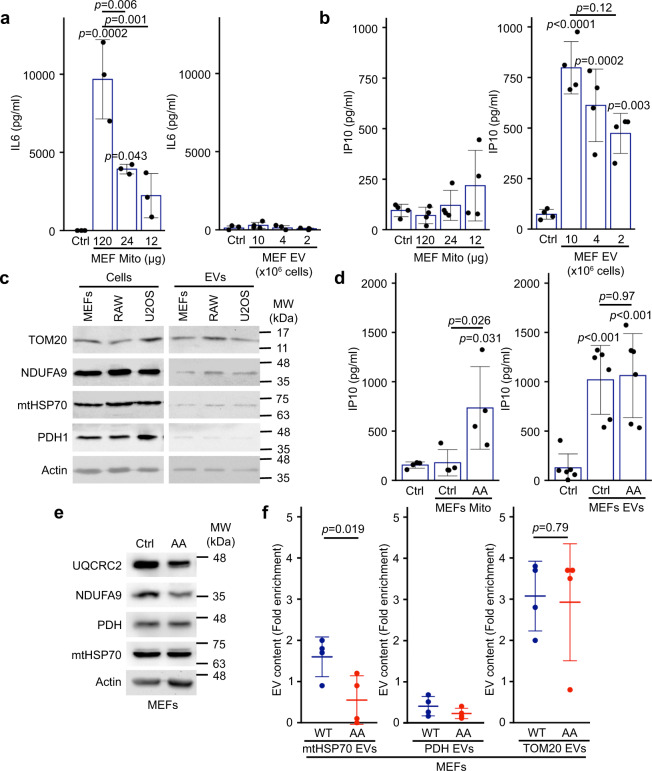
Fig. 1. Mitochondria and EVs activate distinct pro-inflammatory cytokines.
a, b Extracellular mitochondria induce the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Mitochondria (Mito)(isolated from MEFs) or EVs (isolated by differential centrifugation from the media of MEFs grown for 24 h in EV-depleted media) were added to RAW cells in their culture media. The release of IL6 (a) and IP10 (b) into culture media was measured by ELISA 24 h. Individual points represent independent experiments (a, n = 3; b, n = 4). Bars show the average ± SD. One-way ANOVA. c Representative western blot showing the amount of the specified mitochondrial proteins in the indicated cell types (20 µg) vs their EVs (5 µg). TOM20, outer membrane protein; NDUFA9, Complex I subunit; mtHSP70 matrix protein associated with the IM; PDH, matrix protein. Actin is used as a control, as it has been shown to associate with EVs. d AA-treated MEFs mitochondria stimulate IP10 production. RAW cells were treated as above with EVs (from 10 × 106 cells) and mitochondria (12 µg) isolated from Control or AA-treated MEFs, and IP10 release in culture media measured by ELISA. Individual points represent independent experiments (mitochondria, n = 4; EVs, n = 6). Bars show the average ± SD. One-way ANOVA. e AA treatment of WT MEFs causes the selective degradation of mitochondrial proteins. MEFs were treated with AA for 24 h and the indicated mitochondrial proteins analysed by western blot. f Enrichment of the indicated mitochondrial proteins in EVs was measured by western blot in Control (blue) and AA-treated (24 h, Red) WT MEFs. Individual points represent independent experiments (n = 4). Bars show the average ± SD. Two-sided t-test).