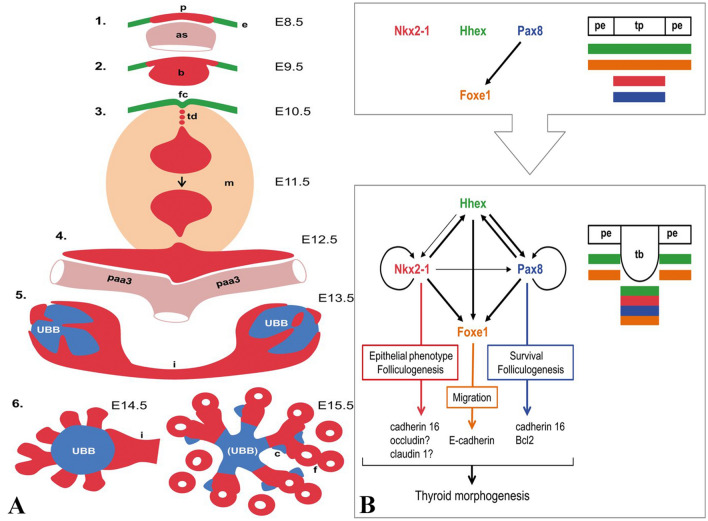
Fig. 1.
THYROID DEVELOPMENT: a Mouse thyroid development by day and stage beginning with the pharyngeal endoderm (e) coalescing into the placode (p) on the cranial aspect of the aortic sac (as) then to the bud (b). The bud detaches and leaves the foramen caecum (fc) with a thyroglossal duct attached (td) and surrounded by mesenchyme (m) followed by bifurcation along the third pharyngeal arteries (paa3). The endodermally derived UBBs from the lateral thyroid anlagen fuse with the thyroid or more appropriately are surrounded by the thyroid and the isthmus forms (i). Lobe growth occurs by the projection of parenchymal cords emanating from the UBB and the conversion of these solid cords into microfollicles (f). C-cells (c) then migrate along the cords at E15.5. b The major transcription factors involved in all aspects of thyroid development include Nkx2-1, Hhex, Pax8, and Foxe1. At the placode (p) stage surrounded by the pharyngeal endoderm (pe), these factors are co-expressed independently with the exception of Foxe1 that requires Pax8. As the bud forms (tb), all factors except for Foxe1 co-regulate the others and Nkx2-1 and Pax8 having autoregulation. Nkx2-1, Pax8, and Foxe1 control the expression of adhesion and junctional proteins that may mediate the functions of these three transcription factors. Figures used with permission from the author and publisher: Mikael Nilsson, Henrik Fagman. Development of the thyroid gland. Development 2017 Jun 15;144(12):2123–2140. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.145615