Figure 1.
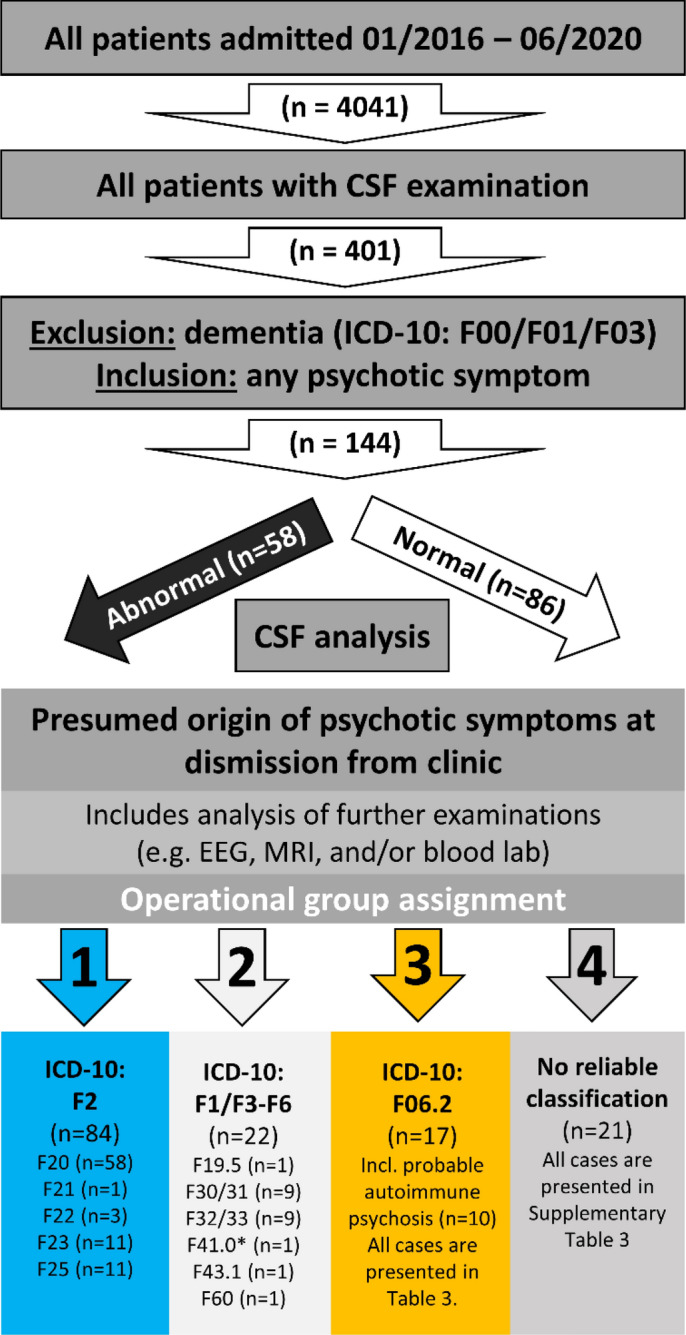
Study diagram. The study diagram shows the workflow of this retrospective analysis of n = 4041 psychiatric inpatient cases. After exclusion of cases with discharge diagnosis of dementia n = 144 cases with any psychotic symptoms and available CSF analysis were identified. These cases were dichotomized into abnormal vs. normal CSF results (for details, see Fig. 2), based on available CSF results. All cases were analyzed in detail and then operationally assigned to one of four groups, taking further examination results into account. All F2 cases constitute the first group (n = 84). The second group consists of other psychiatric disorders with psychotic symptoms (F1/F3-F6) with the exact ICD-10 diagnosis named below. (*) The F41.0 case presented with an additional Attenuated Psychosis Syndrome (as described in DSM5) with hallucinations. The F06.2 group includes the predefined probable autoimmune psychosis (criteria according to Pollak10, n = 10) and seven additional cases. In 21 cases, the abnormal findings (CSF and furthers) were not sufficient to explain the psychotic symptoms; they were categorized as "no reliable classification" due to lack of clear predefined criteria.
