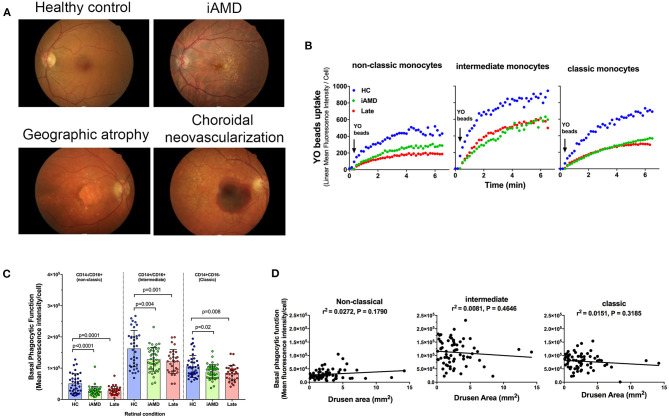
Figure 2.
Monocyte phagocytosis in subjects with AMD. (A) Representative fundus images from a healthy control (normal) subject, person with intermediate AMD (iAMD), geographic atrophy and choroidal neovascularization. (B) A typical example of YO beads uptake curve by three monocyte subsets from a healthy control (HC; blue) a patient with intermediate AMD (green) and a subject with late AMD (red) Fresh human peripheral blood monocytes (PBMCs) were labeled with APC-conjugated CD14 and FITC-conjugated CD16 before the addition of 1 μm YO beads. The YO beads fluorescence intensity was analyzed by real time flow cytometry. (C) Graph showing mean ± standard deviation basal phagocytic function of monocytes subsets isolated from healthy control subjects (HC) (n = 35), subjects with iAMD (iAMD) (n = 61) and subjects with late AMD (n = 30). P-values from One-way ANOVA analysis and Tukey's multiple comparisons tests are shown for comparison between specific groups. (D) Correlations of basal phagocytic function for the three monocyte subtypes compared to drusen area. There was no significant correlation between phagocytosis and drusen area for any of the monocytes examined.