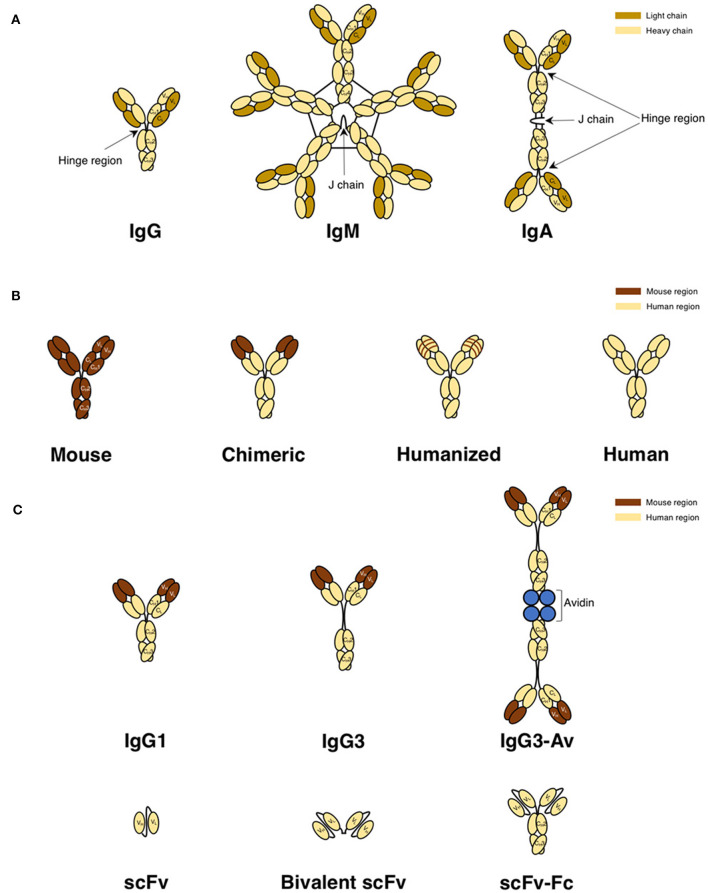
Figure 4.
Antibody classes and derivatives used to target TfR1 for cancer therapy. (A) Naturally occurring antibody formats IgG, IgM, and IgA in mice, rats, and humans. IgG, representing the basic structure of an antibody, is composed of two light and two heavy chains. The light chain is composed of variable light (VL) and constant light (CL) domains. The heavy chain is composed of one variable heavy (VH) domain and three constant heavy domains (CH1, CH2, and CH3) and contains a hinge region between the CH1 and CH2 domains that provides flexibility to the molecule. IgM is a pentamer with a joining (J) chain, but can also be found as a hexamer without a J chain (not shown). IgA is a dimer with a J chain. (B) Representations of a mouse IgG antibody, a mouse/human chimeric antibody with murine variable regions, a CDR-grafted or “humanized” antibody with murine CDRs, and a fully human antibody. (C) Structurally modified human antibody formats. Both the IgG1 and IgG3 are chimeric antibodies that have murine variable regions and human constant regions, while the avidin fusion protein is the chimeric IgG3 with chicken avidin genetically fused to the C-terminus of each heavy chain. Due to the tetrameric structure of avidin, this fusion protein exists as a dimer in solution. The three smaller antibody formats (scFv, divalent scFv, and scFv genetically fused to the Fc fragment) contain all human domains.