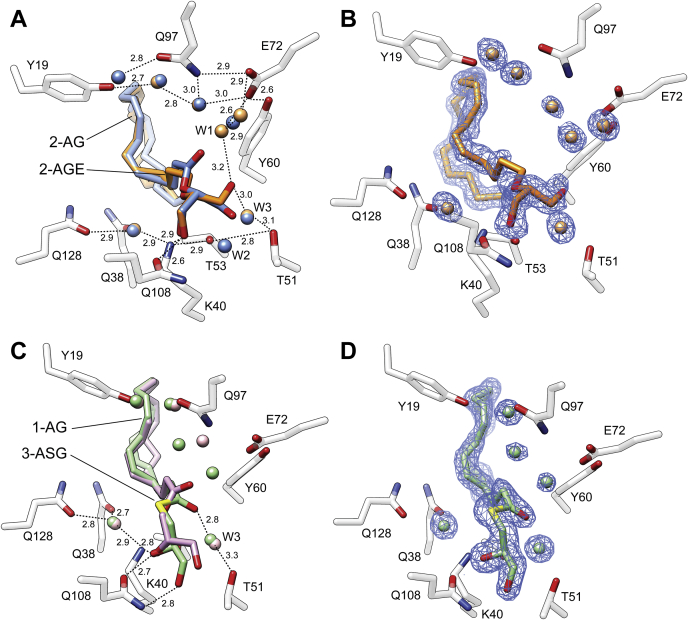
Fig. 5.
Rearrangement of the hydrogen bonding networks upon binding of monoacylglycerol derivatives. A: Comparison of the spatial orientation of 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) (blue) and its derivative lacking the carbonyl oxygen, 2-arachidonoyl glycerol ester (2-AGE, colored orange). B: The 2Fo-Fc electron density maps for 2-AGE and surrounding ordered water molecules. The map was contoured at 1.3 σ. C: Superposition of 1-arachidonoylglycerol (1-AG) (purple) and its derivative, arachidonoyl-3-thio-glycerol (3-ASG), in which carboxyl oxygen was replaced by a sulfur atom (thioester). 3-ASH is colored purple. D: The 2Fo-Fc electron density maps for 1-ASG and surrounding ordered water molecules. The map was contoured at 1.3 σ. In all panels, the ordered water molecules (W) are shown as red spheres and colored in the fashion corresponding to the ligands; dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds. Distances are shown in angstroms.