Fig. 1.
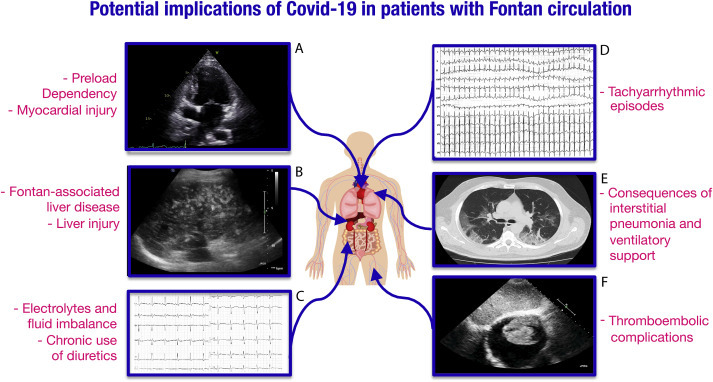
Main potential implications of Coronavirus disease 2019 in patients with Fontan circulation.
Patients with Fontan circulation have a complex physiology and may present multiorgan complications in case of infection. Covid-19-related interstitial pneumonia may raise pulmonary vascular resistance with deleterious effects on pulmonary blood flow in these patients. Moreover, respiratory support techniques including both non-invasive positive-pressure ventilation and mechanical ventilation may reduce the systemic venous return leading to impaired cardiac output in a preload-dependent circulation. Covid-19-related myocardial injury may further interfere the Fontan hemodynamics. Systemic inflammation might easily trigger arrhythmic events in this susceptible population. Gastrointestinal disorders may exacerbate fluid and electrolyte imbalance especially in those on chronic diuretic treatment and trigger arrhythmias. Fontan patients are prone to thromboembolic complication, which are also a known adverse event in Covid-19 patients. Finally, Covid-19-related hepatic damage may superimpose on a Fontan-associated liver disease.
A. Echocardiographic 4-chamber view in a patient with tricuspid atresia palliated with total cavopulmonary connection.
B. Liver fibrosis in a patient with Fontan circulation.
C. ECG of a patient with Fontan circulation and severe hypokaliemia.
D. ECG showing supraventricular tachycardia with a heart rate of 250 bpm in a patient with Fontan circulation.
E. Chest CT in patient with Covid-19 related interstitial pneumonia demonstrating multiple areas of ground glass opacity.
F. Right atrial thrombus in a patient with tricuspid atresia and atrio-pulmonary connection.
