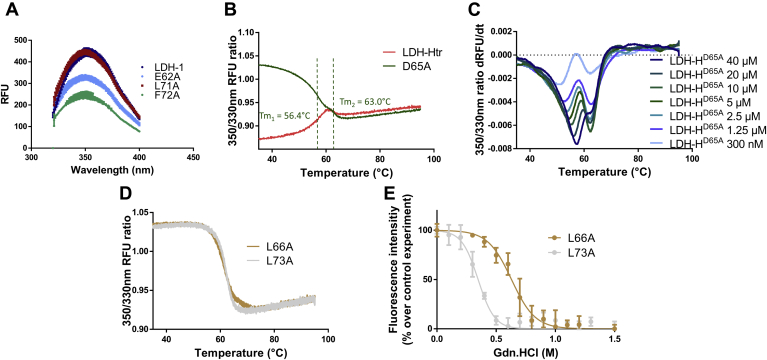
Figure 7.
The exploitation of orthogonal methods highlights the impact of key mutations on LDH-H tetrameric stability.A, tryptophan fluorescence spectra of different LDH-H variants (1.3 μM). λexc = 286 nm (n = 6). B, nanoDSF profiles of LDH-HD65A and LDH-Htr (n = 6). C, nanoDSF profile of LDH-HD65A at different concentrations. Data are represented as the derivative of the 350/330 nm fluorescence ratio to highlight the apparition of the second unfolding event (n = 3). D, nanoDSF profiles of LDH-HL66A and LDH-HL73A (n = 6). E, fluorescence intensity of tetrameric LDH-HL66A and LDH-HL73A at 50 μg/ml (1.3 μM) upon addition of guanidinium·hydrochloride (n = 6). λexc, wavelength of excitation; LDH-H, lactate dehydrogenase heart isozyme; LDH-Htr, LDH-H truncated; nanoDSF, nanoscale differential scanning fluorimetry; RFU, relative fluorescent unit.