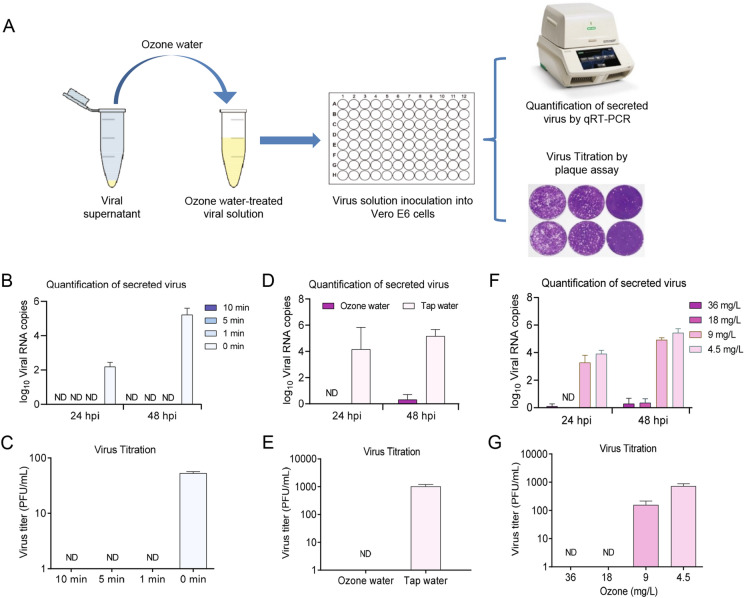
Fig. 1.
Ozonated water inactivates SARS-CoV-2. A Scheme of the experiment. The viral supernatant was incubating with ozone water. After disinfection reaction, the mixture was then inoculated into Vero E6 cells. The secreted viruses in the supernatant were collected at 24 hpi and 48 hpi, respectively, and subjected to qRT-PCR assay. The titers of viruses were determined by viral plaque assay at 96 hpi. B, C Contact time required for ozone water inactivation of SARS-CoV-2. Viral solution (4.0 × 103 PFU/mL) was incubating with ozone water (36 mg/L) for 0, 1, 5, 10 min, respectively. The disinfection efficacy was evaluated by qRT-PCR (B) and viral plaque assay (C). D, E Disinfection capacity of ozone water. A higher PFU viral solution (4.0 × 104 PFU/mL) was incubated with ozone water (36 mg/L ozone) or tap water (0 mg/L ozone), respectively. Similar tests were performed to quantify viral RNA and titers by qRT-PCR (D) and plaque assay (E). F, G Ozone concentration required for ozone water inactivation of SARS-CoV-2. Serially diluted ozone water (36, 18, 9, 4.5 mg/L) was incubating with the viral solution (4.0 × 104 PFU/mL) for 1 min, and the disinfection efficacy was determined by qRT-PCR (F) and viral plaque assay (G), as mentioned above. The data points indicated the averages of triplicate experiments, and the error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). ND: not detected.