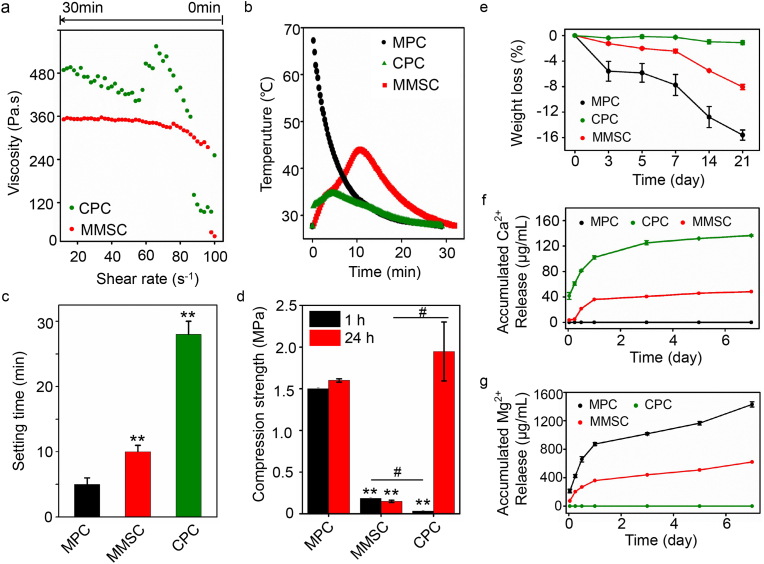
Fig. 4.
Physiochemical properties of MMSC compared with those of the MPC and CPC. (a) The rheological curve showed that the MMSC pastes had a constant and low viscosity, which suggested good rheological properties and practicable injectability. (b) The heat release of MMSC was well-controlled in comparison with MPC suggesting that the microspheres effectively reduced the exothermic reaction (c) The setting time was approximately 10 min in the MMSC, which well-met the requirement of clinical application. (d) Mechanical strength results showed that the compressive strength of the MMSC was stable after setting for 1 h (mean ± SD; n = 3; *significant difference compared with the MPC group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; # significant difference between groups, #p < 0.05). (e) MMSC had a moderate degradation rate with a weight loss of approximately 8 wt% after 21 days (mean ± SD, n = 5). (f, g) Calcium and magnesium ions can be released from the MMSC simultaneously at a moderate rate (mean ± SD, n = 5).