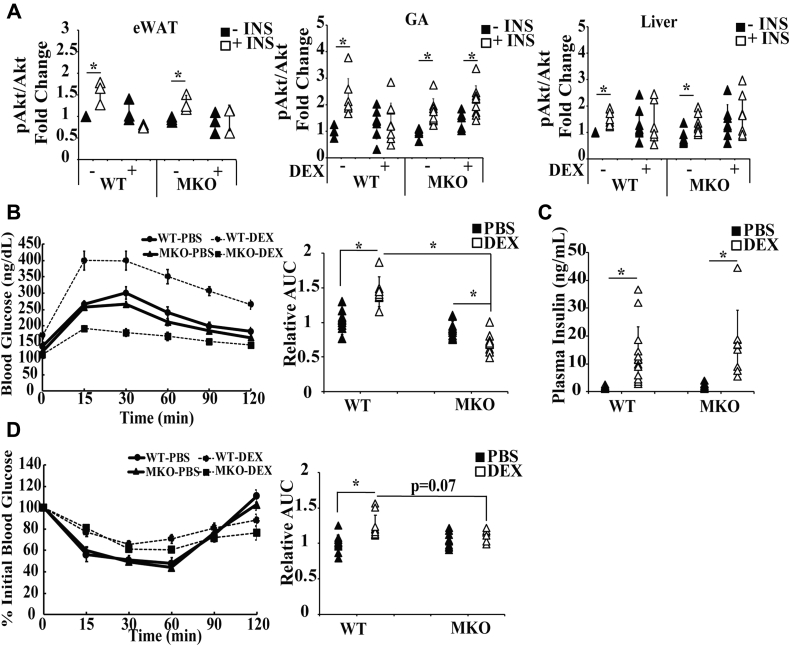
Figure 3.
GC-induced glucose intolerance is compromised in MKO mice.A, male 8-week-old WT and MKO mice were treated with 10 mg/kg of PBS or DEX in drinking water for 1 week. On the last day, mice were injected intraperitoneally with insulin (1 unit/body weight) for 10 min, and then various tissues were collected. ELISA kits were used to monitor the level of Akt and phosphor-Akt in eWAT, liver, and GA muscle. The results are presented as relative pAkt/AKt level. Error bars represent the SD, n = 3 to 9 and ∗p ≤ 0.05 comparing no insulin treatment to insulin treatment. B, male 8-week-old WT mice and MKO mice were treated with 10 mg/kg of DEX for 7 days. On the last day, mice were fasted for 15 h, and the IPGTT was performed. Relative area under curve (AUC) for IPGTT results (relative to PBS-treated WT mice). Error bars represent the SD, n = 6–12 and ∗p ≤ 0.05. C, plasma insulin level was measured before glucose injection (0 min time point). Error bars represent the SD, n = 6 to 12 and ∗p ≤ 0.05. D, ITT was performed in mice as described in Methods. ITT results were depicted as percentage of initial plasma glucose level (the plasma glucose level before insulin injection). Error bars represent the SD, n = 3 to 7. Relative area under curve (AUC) for ITT results (relative to PBS-treated WT mice) is shown. Error bars represent the SD, n = 6 to 11 and ∗p ≤ 0.05. DEX, dexamethasone; IPGTT, intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test; ITT, insulin tolerance test.