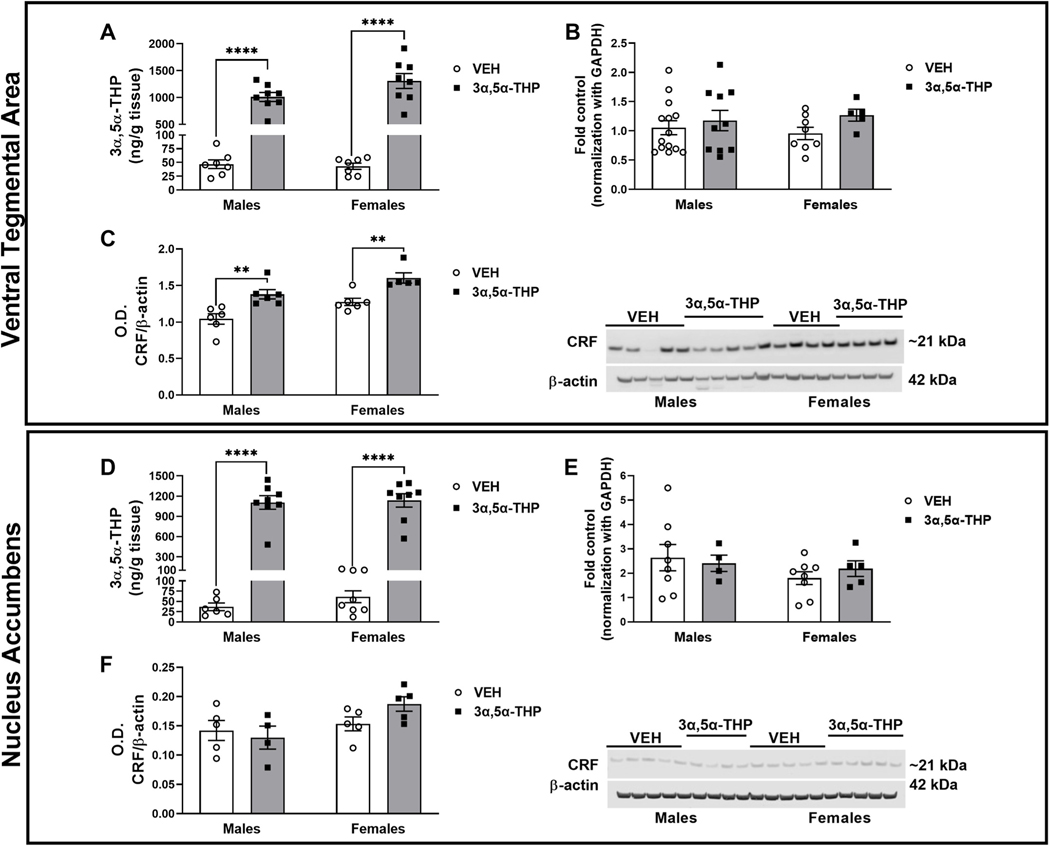
Fig. 4. 3α,5α-THP administration increased CRF peptide levels in ventral tegmental area (VTA), while did not affect CRF signaling in nucleus accumbens (NAc).
Ventral Tegmental Area: A. 3α,5α-THP (15 mg/kg) IP administration increased 3α,5α-THP levels in VTA of male and female rats (males VEH = 46.83 ± 7.94 ng/g tissue vs 3α,5α-THP = 1011 ± 83.39 ng/g tissue, p < 0.0001; females VEH = 43.11 ± 5.7 ng/g tissue vs 3α,5α-THP = 1308 ± 138.7 ng/g tissue, p < 0.0001) (n = 6–8 rats per group). B. qPCR analysis did not show any sex or treatment difference in CRF mRNA expression (n = 5–12 rats per group). C. Western blotting analysis showed an increase in both male and female rats following 3α,5α-THP injection (V males VEH = 1.043 ± 0.07 vs 3α,5α-THP = 1.380 ± 0.06, p = 0.0062; females VEH = 1.276 ± 0.05 vs females 3α,5α-THP = 1.602 ± 0.07, p = 0.0115) (n = 5–6 per group). Nucleus accumbens: D. 3α,5α-THP (15 mg/kg) IP administration increased 3α,5α-THP levels in male and female rats (males VEH = 36.78 ± 9.3 ng/g tissue vs 3α,5α-THP = 1105 ± 100.6 ng/g tissue, p < 0.0001; females VEH = 61.46 ± 14.51 ng/g tissue vs 3α,5α-THP = 1136 ± 100.7 ng/g tissue, p < 0.0001) (n = 6–8 rats per group). E. qPCR analysis did not show any sex or treatment differences in CRF mRNA expression (n = 4–8 rats per group). F. Western blotting analysis did not detect any change in CRF protein levels due by sex or treatment with 3α,5α-THP (n = 5–6 per group). Significant effect was found using Two-Way ANOVA, followed by Tukey HSD test, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. VEH = rats treated with vehicle; 3α,5α-THP = rats treated with 3α,5α-THP.