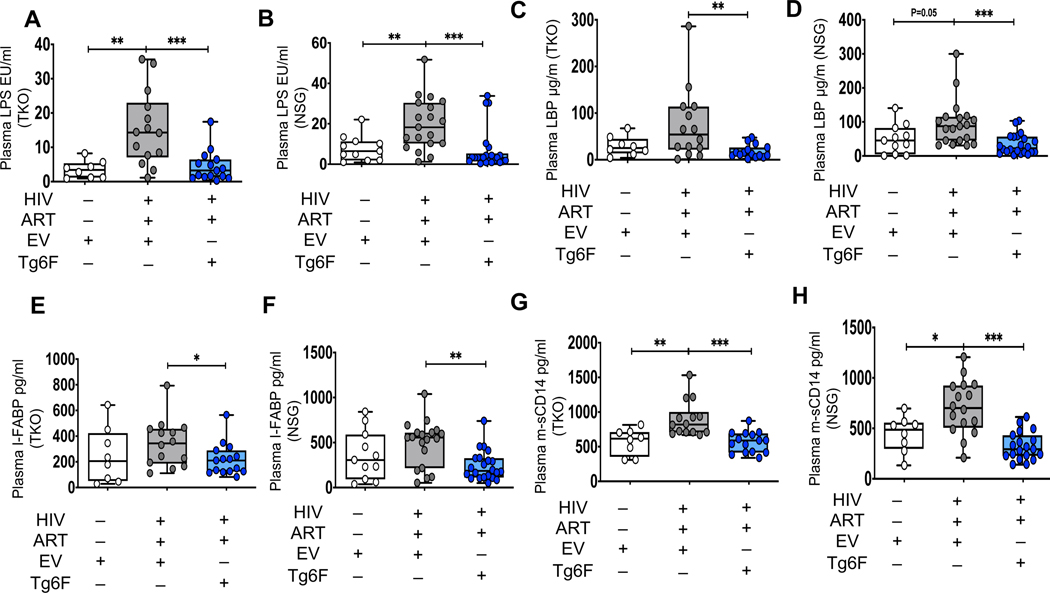
Figure 2. Tg6F attenuates microbial translocation and gut barrier dysfunction in independent humanized mouse models of chronic treated HIV infection.
TKO C57 (n=38) and NSG (n=52) humanized mice were constructed, infected with HIV and treated with ART, control transgenic tomato concentrate (EV) or Tg6F as described in Figure 1. Whole blood from each mouse was collected, plasma was prepared and murine plasma biomarkers of bacterial translocation and gut barrier dysfunction, that are known predictors of morbidity in chronic treated HIV, were determined. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was quantified by endpoint chromogenic limulus amoebocyte lysate assay. Lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP) and Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein (I-FABP) were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Murine plasma sCD14 levels were determined by Luminex. Data represent box and whiskers with minimum, median and maximum values of murine plasma LPS (endotoxin units per milliliter; EU/mL) (A, B), LBP (μg/ml) (C, D), I-FABP (E, F) and plasma murine sCD14 (pg/ml) (G, H) in TKO (A, C, E, G) and NSG (B, D, F, H) humanized mice (n = 8–22 mice per group). The Mann-Whitney test was used to compare 2 groups (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).