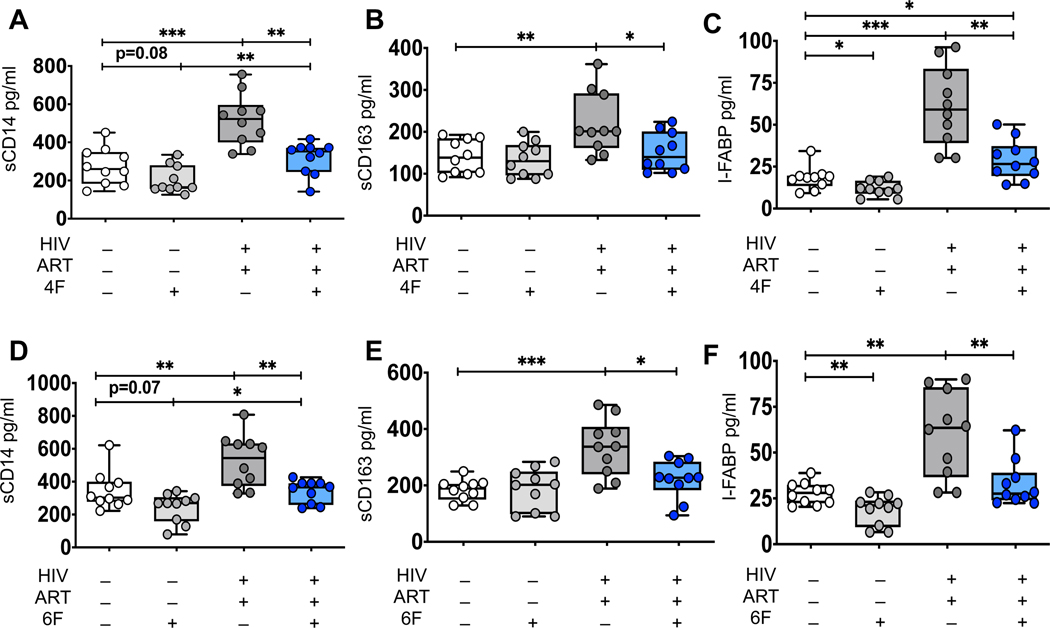
Figure 4. ApoA-I mimetic peptides attenuates ex vivo biomarkers of immune activation and gut injury derived from gut explants of uninfected and HIV infected ART-treated participants.
Gut biopsies were obtained from uninfected (n=10) and HIV infected participants on potent ART (n=10) and gut explants were treated with 4F or 6F apoA-I mimetic peptides or sham peptide at concentration 100 μg/ml for 72 hours as in methods. Supernatants were collected and protein levels of secreted sCD14, sCD163 were determined in supernatants by Luminex immunoassays. I-FABP was determined by ELISA. The first group included gut explants from uninfected participants treated with sham peptide, white boxes and datapoints, HIV- (n=10). The second group included gut explants from uninfected participants treated with 4F (A-C) or 6F (D-F), light grey boxes and datapoints, HIV- (n=10). The third group included gut explants from HIV infected participants who received ART; these explants were treated with sham peptide, dark grey boxes and datapoints, HIV+ART+ (n=10). The fourth group included gut explants from HIV infected participants who received ART; these explants were treated with 4F (A-C) or 6F (D-F), blue boxes and datapoints, HIV+ART+4F+ or HIV+ART+6F+ (n=10). Gut biopsies from the same participants were used for experiments with 4F and 6F. Data represent box and whiskers with minimum, median and maximum values of sCD14 (A, D), sCD163 (B, E) and I-FABP (C, F) (n=10 per group). Datapoints represent mean of 3 gut biopsies per participant. The Mann-Whitney test was used to compare 2 groups (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).