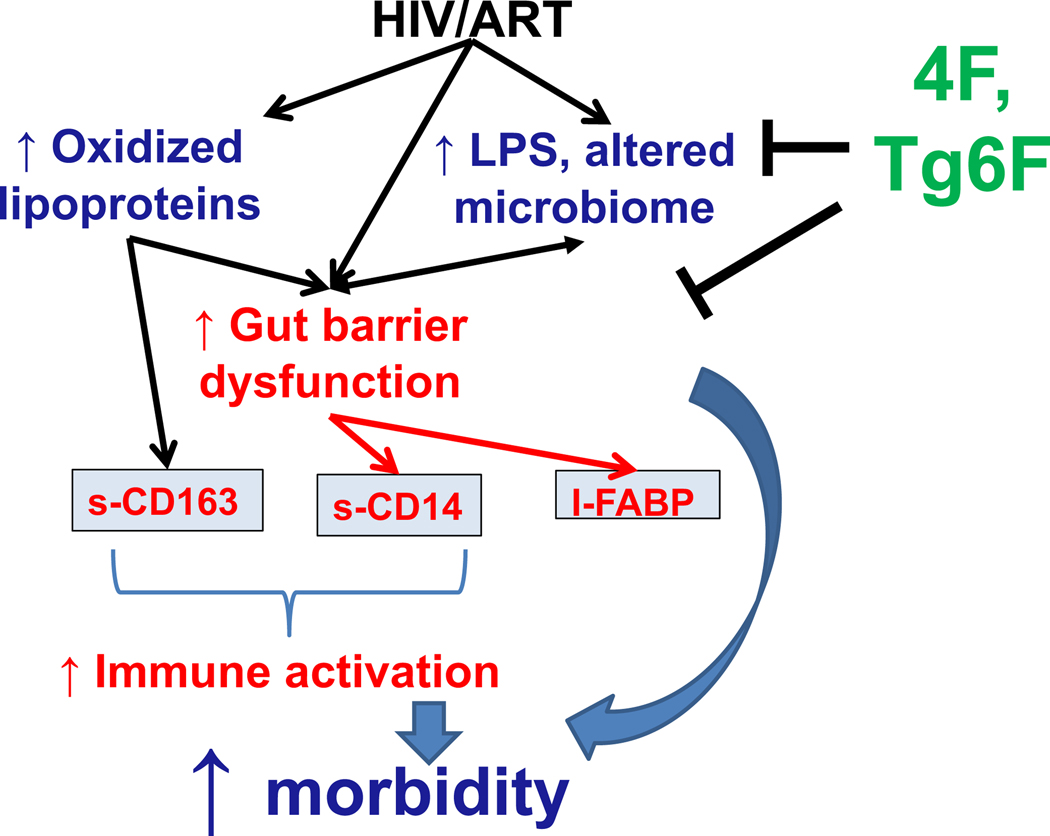
Figure 5. Overall Hypothesis.
HIV, ART, oxidized lipoproteins (HDLox, LDLox) and microbial products (such as LPS) collectively drive gut barrier dysfunction (increased circulating I-FABP) and macrophage activation (increased circulating sCD14, sCD163) in chronic treated HIV. ApoA-I mimetic peptides such as 4F and Tg6F bind LPS and attenuate formation of oxidized lipoproteins in the gut, reducing macrophage activation, gut barrier dysfunction and ultimately morbidity in chronic treated HIV.