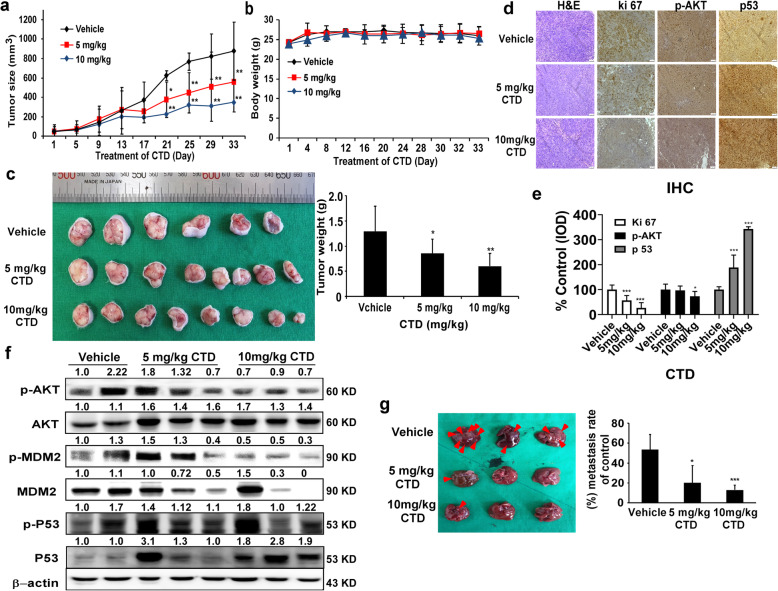
Fig. 8.
CTD inhibits tumor growth in vivo. a The effect of CTD on the volume of CDX tumors was plotted over 30 days (HCT-116). Vehicle and CTD (5 or 10 mg/kg) were administered intraperitoneally. The tumor volume was measured twice a week. b The body weight was stable after CTD treatment indicating a lack of toxicity at these doses. c The photographs (left) show tumors from CDX mice treated with vehicle or CTD (5 or 10 mg/kg), and the weights of the tumors were quantified and expressed as the treatment groups compared with the vehicle-treated group (right). d The expressions of Ki-67, p-AKT, and p53 were examined by IHC analysis (100× magnification). e The quantitation of the protein expression from IHC staining. The values are quantified from IHC staining and expressed as the treatment groups compared with the vehicle-treated control group. The data are expressed as IOD. f CTD affects the expression of AKT-MDM2-p53 signaling proteins in the CDX tumor tissues. The tumor tissues were analyzed by western blotting. g Left, the representative images of the excised livers after the mice were sacrificed (arrows indicate the metastatic nodules). Right, the graph showing the number of surface metastatic foci in the livers. All data are shown as the mean value ± SD. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001) indicate a significant decrease compared to the control