Figure 2.
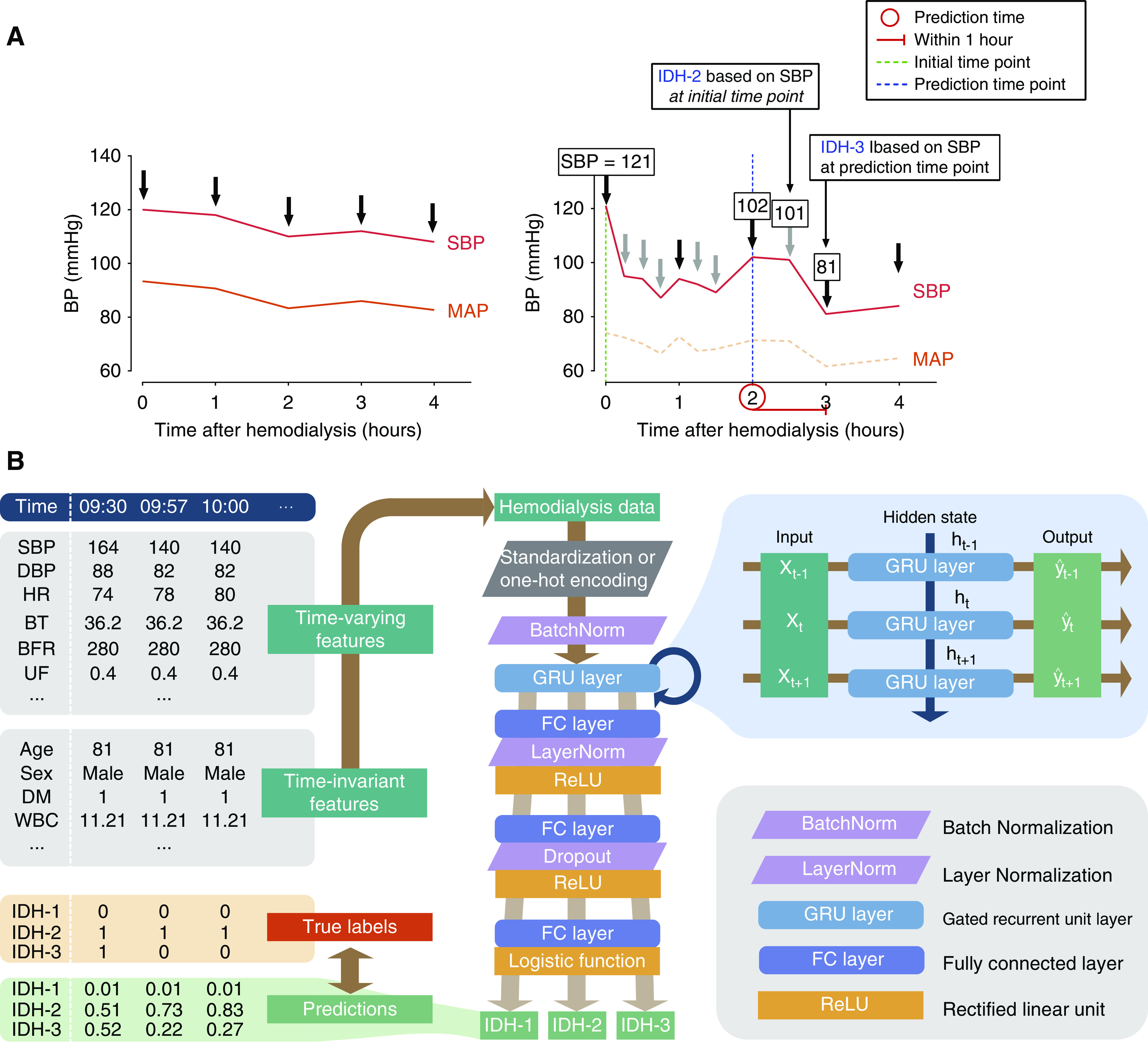
Development of recurrent neural network model. (A) Illustrative example of sessions with stable vital signs (left) and intradialytic hypotension (IDH) (right). The risk of IDH within 1 hour at a certain time point (red circle) was calculated. When IDH was defined as a decrease in systolic BP ≥20 mm Hg and/or a decrease in mean arterial pressure ≥10 mm Hg, the reference BPs were determined at initial (IDH-2) or prediction (IDH-3) time point. Black and gray arrows indicate routine and additional monitoring of BPs, respectively. (B) Architecture of the proposed recurrent neural network model. Briefly, time-varying and time-invariant features were embedded in the cells with multilayer perceptron. The deepening effect was obtained by inserting fully connected layers between cells, and the learning was stabilized using the layer normalization. IDH-1, intradialytic hypotension defined as nadir systolic BP <90 mm Hg; IDH-2, intradialytic hypotension defined as decrease in systolic BP ≥20 mm Hg and/or decrease in mean arterial pressure ≥10 mm Hg on the basis of BP at initial time point; IDH-3, intradialytic hypotension defined as decrease in systolic BP ≥20 mm Hg and/or decrease in mean arterial pressure ≥10 mm Hg on the basis of BP at prediction time point. SBP, systolic BP; DBP, diastolic BP; HR, heart rate; BT, body temperature; BFR, blood flow rate; UF, ultrafiltration; DM, diabetes mellitus; WBC, white blood cell count; BatchNorm, batch normalization; LayerNorm, layer normalization; GRU, gated recurrent unit; FC, fully connected; ReLU, rectified linear unit.
