Fig. 2.
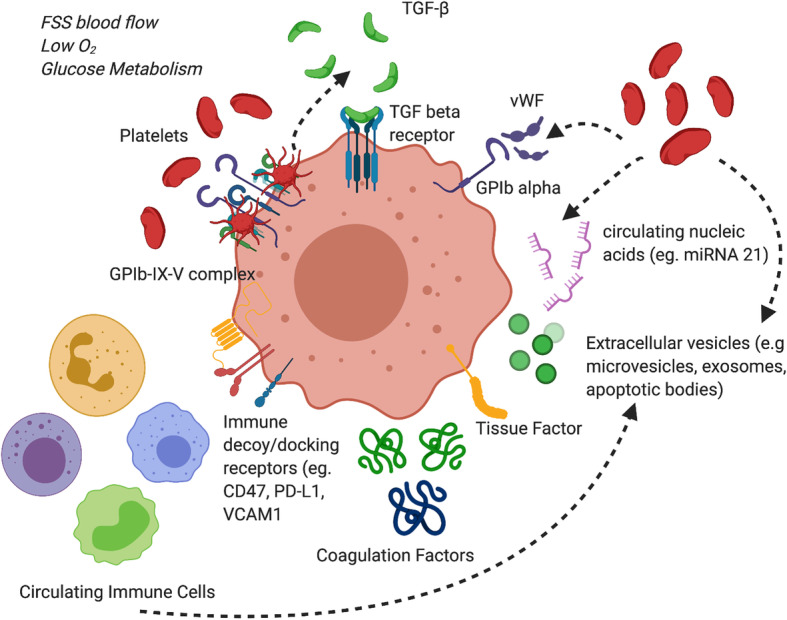
CTCs interactions with constituents of the blood circulation. CTCs are exposed to a number of influencing factors while in circulation including fluid sheer stress (FSS), hypoxia, nutrient starvation/glucose metabolism. Platelets, coagulation proteins and immune cells provide either direct or indirect contacts with CTCs to aid in their survival. Platelets are a rich source of TGF-β which promotes EMT. Platelets and coagulation proteins also protect CTCs from FSS through the creation of a rich microthrombi surrounding CTCs. CTCs evade immune detection through the expression of immune decoy receptors such as CD47 and PD-L1. These cells, proteins and circulating nucleic acids/extracellular vesicles can influence not only the phenotype of the CTC in circulation but also its molecular make up and cellular fate within the peripheral blood circulation
