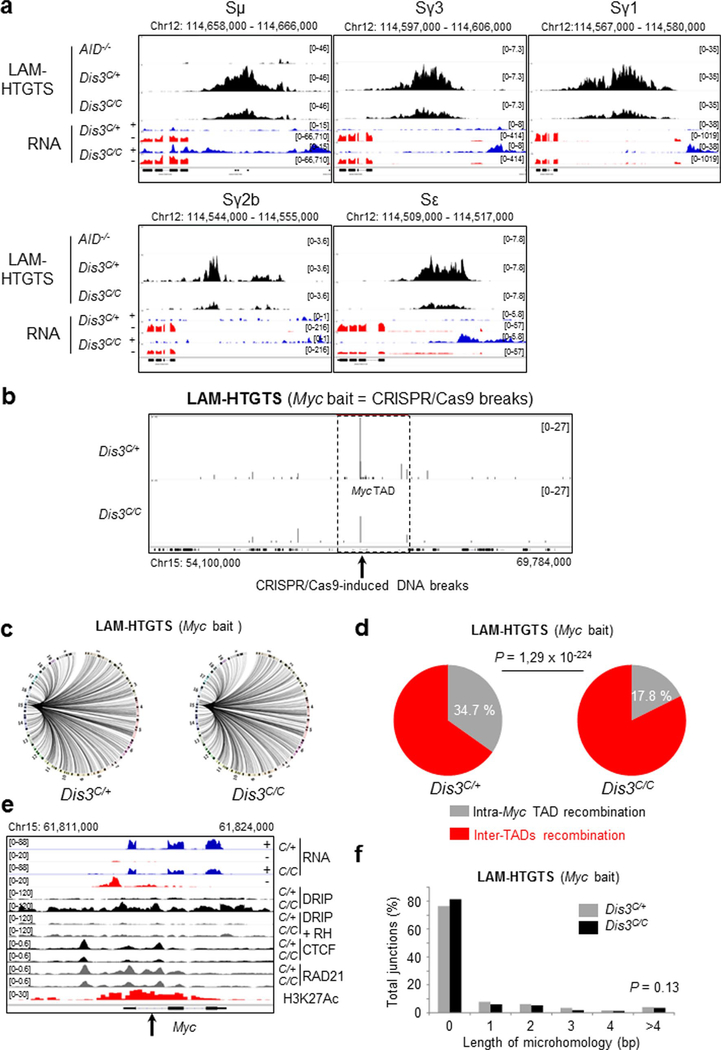
Extended Data Fig. 9 |. Decrease physiological DNA double strand breaks at Igh switch regions, and increase chromosomal translocations at the Myc tAD in the absence of DIS3.
a. LAM-HTGTS from AID−/−, Rosacre/+ Dis3C/+, and Rosacre/+ Dis3C/C activated B cells at Sμ, Sγ3, Sγ1, Sγ2b, and Sε regions with corresponding RNA-seq (combined data from 3 independent experiments). b to f. CRISPR/Cas9-induced DNA breaks and processing at the Myc locus Primary B cells (Rosacre/+ Dis3C/+ and Rosacre/+ Dis3C/C) were infected during in vitro stimulation with CRISPR/Cas9 retrovirus to induce DNA breaks at the Myc locus. DNA junctions were analyzed by LAM-HTGTS using Myc bait (2 independent experiments with 2 or 3 biological replicates and 3 independent libraries used for sequencing). b. DNA breaks induced by CRISPR/Cas9 at Myc intron 1 and captured using Myc bait. Black arrow indicates the position of CRISPR/Cas9-induced DNA breaks. Myc TAD is outlined by dashed lines. c. Circos plots showing global DNA translocations. d. 2 fold decrease in intra-TAD recombination in the absence of DIS3. The proportion of intra-Myc TAD recombination and inter-TADs translocations is shown (total DNA junctions of 8,122 in Dis3C/+ and 5,529 in Dis3C/C), χ2 two-tailed proportions test. e. NcRNAs and DNA:RNA hybrids accumulation at the Myc locus decrease CTCF/RAD21 binding. RNA-seq data show aTSS and intronic ncRNAs accumulation in Dis3C/C cells, DRIP displays increased DNA:RNA hybrids, while CTCF and RAD21 ChIP-seq reveal decreased CTCF/RAD21 binding. Black arrow indicates CRISPR/Cas9-induced DNA breaks. f. Global analysis of the DNA junctions from Myc LAM-HTGTS, showing length and frequencies of microhomology overlapping bait and prey sequences. All DNA junctions from 3 experiments were combined and the distributions of insertions were evaluated by χ2 two-tailed proportions test (comparing DNA junctions with microhomology length >4 to the total junctions between Rosacre/+ Dis3C/+ and Rosacre/+ Dis3C/C cells).