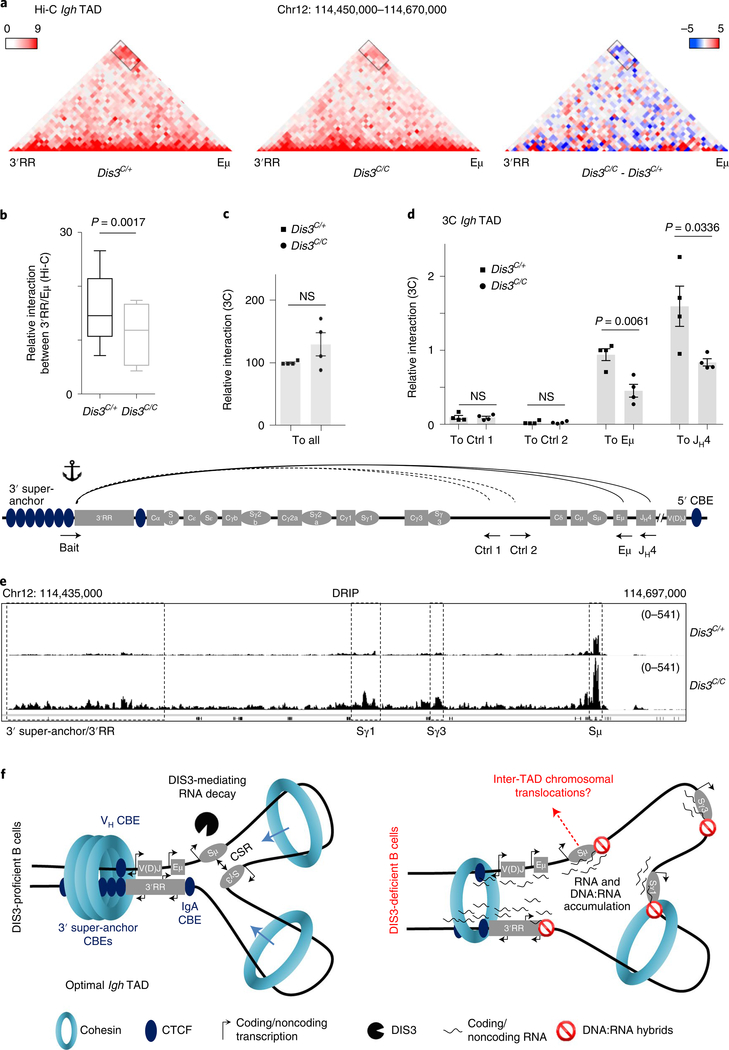
Fig. 4 |. DIS3 regulates DNA:RNA accumulation and Igh tAD formation during B-cell activation.
a–d, Evaluation of Igh TAD architecture in DIS3-deficient cells. Rosacre/+Dis3C/+ and Rosacre/+Dis3C/C B cells were stimulated and analyzed at an early time point (24 h of IL-4 treatment) for Hi-C (four independent experiments with three biological replicates) and 3C (two independent experiments with four biological replicates) experiments. Combined data were used for Hi-C analyses and Hi-C visualization was performed using Juicebox. a, Decreased DNA interactions at the Igh TAD in the absence of DIS3. Interactions between the 3′RR super-enhancer and the Eμ intronic enhancer (black rectangle) in Rosacre/+Dis3C/+ and Rosacre/+Dis3C/C activated B cells are shown (left and middle; relative interaction values are in red). The decreased interaction between the 3′RR and Eμ is shown using the subtraction method from Juicebox, calculated by subtracting the control value from the observed value (right; relative gained interactions are in red and the relative lost interactions are in blue). b, The interaction values between the 3′ super-anchor/3′RR region and Eμ/Sμ regions were extracted from Hi-C data and quantified using a two-tailed paired t-test. The box and whiskers plots represent these values, the bottom and top whiskers represent the minimum and maximum scores, respectively, outside the interquartile range. The box plots show the lower quartile, median and upper quartile. c, Schematic of the 3C experiment (bottom, not on scale). Bait located at the end of the 3′RR and beginning of the 3′ super-anchor was used, in combination with control intergenic regions, Eμ, or JH4 interacting regions. Due to the use of LAM-HTGTS to specifically enrich Igh TAD interactions, the interacting regions contain a universal reverse adaptor at their 3′ end. The interaction between the bait and all these interactions using the universal reverse primer is shown as control (ctrl) in Dis3C/+ (squares) and Dis3C/C (dots), two-tailed unpaired t-test. d, The 3′RR/intergenic control 1, 3′RR/intergenic control 2, 3′RR/Eμ and 3′RR/JH4 relative interactions were quantified by 3C experiments followed by qPCR. Bar graphs from c and d represent the mean ± s.e.m. from four biological replicates; each point is the mean for one biological replicate, two-tailed unpaired t-test. Note the JH4 restriction fragment can be either germline or create a V(D)J exon, because the restriction site is located upstream of the recombination signal sequence. e, Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) tracks showing the accumulation of DNA:RNA hybrids at the Igh locus. DNA:RNA hybrids strongly accumulate at switch (S) regions, particularly at Sμ donor region, Sγ1, Sγ3 and at the 3′ super-anchor/3′RR super-enhancer. f, Model postulating DIS3-mediated processing of ncRNAs is important for efficient Igh TAD formation and CSR. Left: the Igh locus contains a 3′ super-anchor composed of multiple CBEs, which is critical for loop extrusion during CSR. At the 5′ extremity of VH genes different CBEs are found and stabilize the Igh TAD in concert with the 3′ super-anchor. Inside the Igh TAD, critical interactions allow an optimal CSR, including Eμ−3′RR super-enhancer interaction. DIS3 is necessary to process the different ncRNAs that are strongly expressed as eRNAs, germline transcripts and CTCF-overlapping RNAs during B-cell activation, ultimately contributing to the formation of an optimal Igh TAD necessary for CSR. Right: in the absence of DIS3, an accumulation of ncRNAs and DNA:RNA hybrids is observed, which decreases CTCF and RAD21 localization to their cognate DNA targets. We propose that these ncRNAs and DNA:RNA hybrids impede cohesin-mediated scanning/loop extrusion and perturb Igh TAD stabilization, in particular the 3′RR/Eμ interaction. This phenomenon contributes to decreased CSR and potentially exposes Sμ DNA breaks to inter-TAD recombination, that is, translocations.