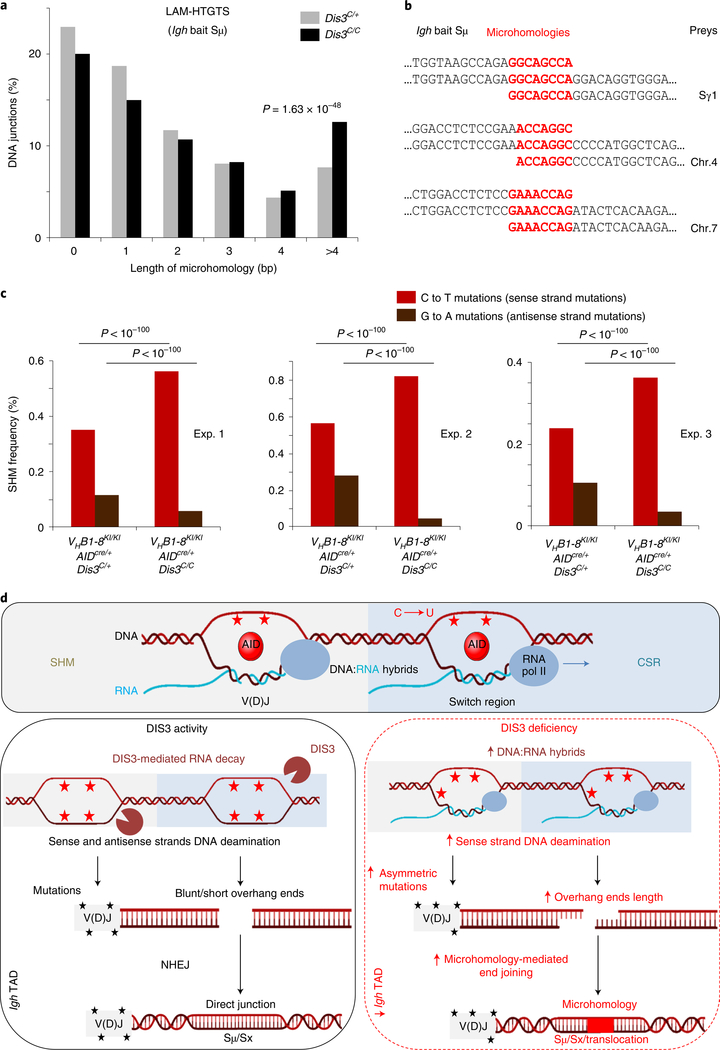
Fig. 6 |. DIS3-sensitive RNA processing influences DNA repair mechanisms and distribution of physiological mutations in activated B cells.
a,b, Microhomology-mediated DNA repair. a, Global analysis of the DNA junctions from Igh LAM-HTGTS showing the length and frequencies of microhomologies overlapping the Igh bait (Sμ) and the prey sequences. All DNA junctions from three independent experiments were combined and the distributions of microhomology-mediated repair evaluated by a χ2 two-tailed proportions test (comparing DNA junctions with microhomology length of >4 bp to the total junctions between Rosacre/+Dis3C/+ and Rosacre/+Dis3C/C cells). b, Examples of microhomology-containing DNA junctions from Rosacre/+Dis3C/C B cells at physiological CSR and translocation junctions. SHM analyses in DIS3-deficient cells. c, Quantification of C and G mutation frequencies in GC B cells. Three pairs of VHB1–8KI/KIAIDcre/+Dis3C/+ and VHB1–8KI/KIAIDcre/+Dis3C/C mice were used. Analyses were performed at the JH gene from the VHB1–8 allele. χ2 two-tailed proportions tests were used to compare the number of C to T mutations relative to the total number of C’s sequenced and the number of G to A mutations compared to the total number of G’s sequenced. d, Proposed model. Top: during SHM and CSR, germline/sense transcripts are expressed at the Igh locus, leading to exposure of the sense single-stranded DNA to AID mutagenic activity (C to U deamination; red stars) as a result of DNA:RNA-associated single-stranded DNA exposure. Bottom left: DIS3 processed sense RNAs, providing AID accessibility to both DNA strands during CSR and SHM. At V(D)J regions, the ratio of sense to antisense mutations (black stars) is physiologically distributed. At switch regions, AID-initiated DNA breaks are equally distributed and frequently generate blunt ends or short overhang DNA extremities. NHEJ is the main DNA repair mechanism, resulting in direct DNA junctions (or short microhomologies). Bottom right: DIS3-deficient cells showed defects in the ability to process DNA-associated RNAs, which increases DNA:RNA hybrids and sense strand DNA deamination. At V(D)J regions, the SHM frequencies were increased on the sense DNA strand and decreased on the antisense strand. At switch regions, this DNA:RNA hybrid accumulation facilitated the creation of DNA with overhang ends and subsequent ligation between complementary sequences, resulting in increased microhomology-mediated DNA repair between switch regions (Sμ and Sx acceptor) or Sμ and translocation partners. Note that the Igh TAD organization was optimal in the presence of DIS3 activity, while intra-Igh TAD interactions between the 3′RR super-enhancer and Eμ were decreased in DIS3-deficient cells.