FIGURE 3.
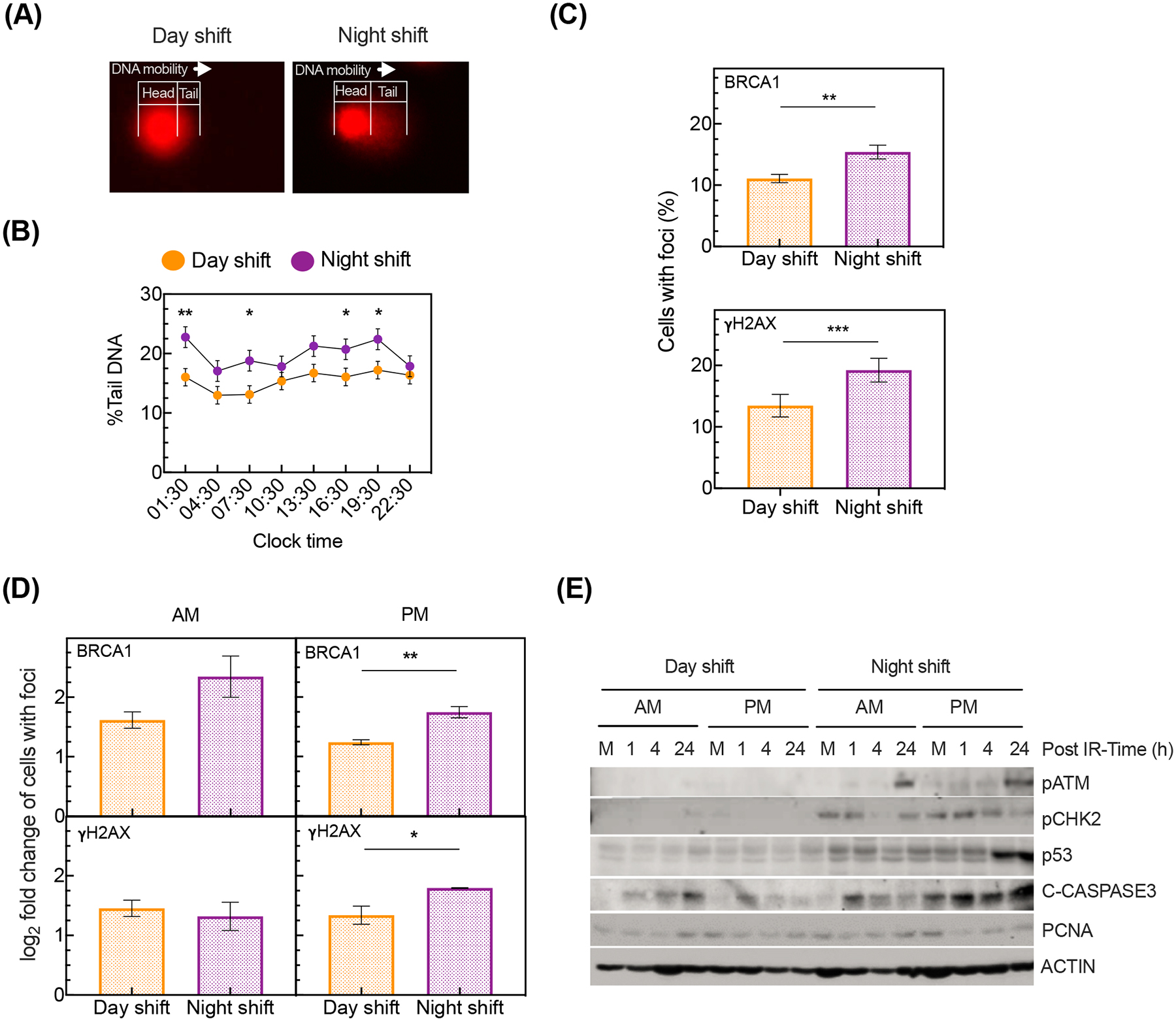
DNA damage under 24-hour constant routine after exposure to simulated day or night shift schedule. (A) Representative DNA migration (head to tail) in leukocytes after simulated day shift (left) versus night shift (right) as assessed with alkaline comet assay. (B) Percentage (mean ± SE) of tail genomic DNA across the 24-hour constant routine, after simulated day shift or night shift (F7,70=4.55, p<0.001, mixed-effects ANOVA condition by time interaction; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, pairwise contrasts). (C) Immunofluorescence quantification of leukocytes with BRCA1 (top) and γH2AX (bottom) foci averaged over the 24-hour constant routine after simulated day or night shift (**p<0.01, ***p<0.001, two-sample t-test). The y-axis indicates the average percentage ± SE. (D) Immunofluorescence quantification of BRCA1 (top) and γH2AX (bottom) foci in leukocytes upon IR treatment of samples collected at 07:30 (AM) or 19:30 (PM) during the 24-hour constant routine after simulated day or night shift (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, two-sample t-test). The y-axis indicates log2 fold change ± SE of the number of foci in IR treated cells versus untreated controls. (E) Representative immunoblot of the DNA damage response upon IR exposure of samples collected at 07:30 (AM) or 19:30 (PM) during the 24-hour constant routine after a simulated day or night shift. M denotes “mock” (i.e., sample not exposed to IR).
