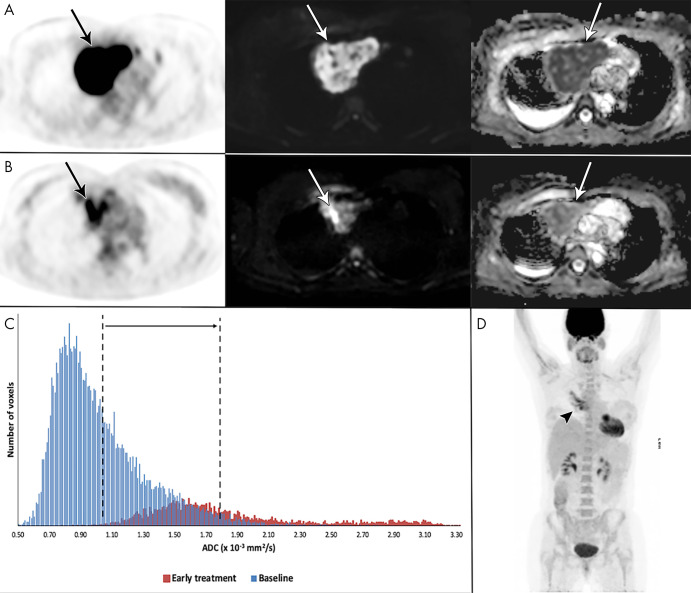
Figure 3:
Example of a 41-year-old woman with stage I primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma. A, Mediastinal mass (arrow) with high fluorine 18 (18F) fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake at 18F-FDG PET/CT (left), high b1000 signal at diffusion-weighted (DW) imaging (middle), and low signal on apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map (right). B, After 2 weeks, 18F-FDG uptake of the mass (arrow) was in keeping with good partial response. DW imaging shows decreased signal on the b1000 images and marked increase of ADC (from 1.02 to 1.80 × 10−3 mm2/sec), confirmed on, C, the ADC histogram, indicating good outcome. D, End-of-treatment 18F-FDG PET/CT shows inflammatory changes (arrowhead), yet complete remission, which was maintained until the end of follow-up.