Fig. 3 |. Drug administration in zebrafish.
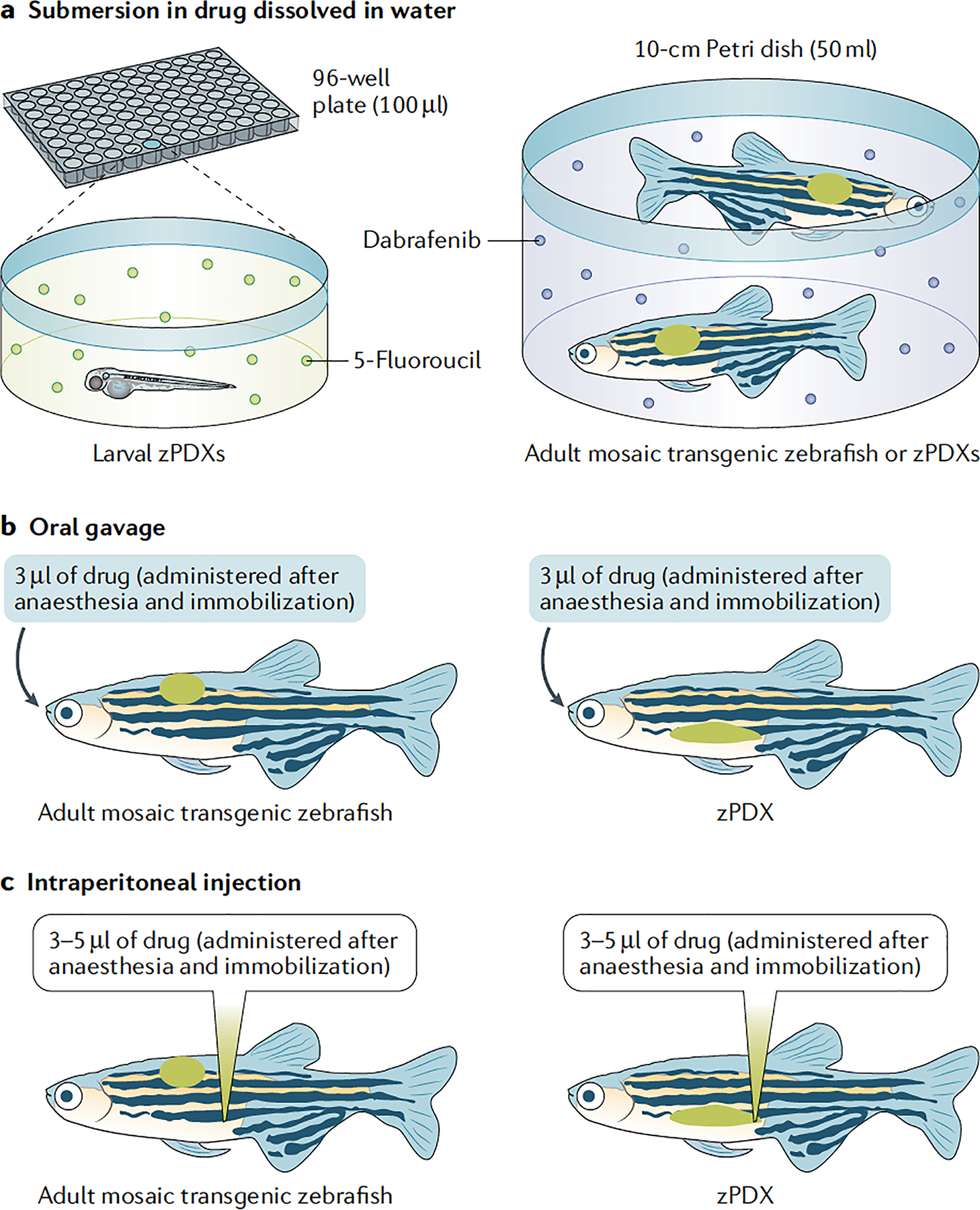
a | Submersion in a water and drug solution is used to treat larval zebrafish patient-derived xenografts (zPDXs) (10–20 24-hour post-fertilization embryos per well in a 24-well plate or one embryo per 96-well plate) or adult avatars (two adults in a 10-cm Petri dish). Example compounds shown were used by Fior et al.13 (5-fluorouracil treatment of larvae) and Ablain et al.12 (treatment of adults with the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib). b | Oral gavage can also be used to treat adult avatars (mosaic transgenic zebrafish or zPDXs). Zebrafish are anaesthetized and immobilized using MS-222 alone or in combination with isoflurane. Oral gavage using a syringe with flexible tubing allows ~3 μl of drug solution to be dispensed (described by Dang et al.79). c | Intraperitoneal injection is another alternative to treat adult avatars (mosaic transgenic zebrafish or zPDXs). Zebrafish are anaesthetized and immobilized using MS-222 or MS-222 and isoflurane. Free-hand injections are performed with 10-μl capacity syringes to deliver up to 5 μl of drug solution. Approximately 3–5 μl is the tolerable range reported14,79.
